Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the previous problem if the paperweight is inverted at its place so that the spherical surface touches the paper.
उत्तर
Given,
Taking the radius of the paperweight as its thickness = 3 cm
Refractive index of the paperweight (μg) = 3/2
Refractive index of the air (μ1) = 1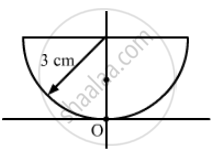
Image shift is given by:
\[∆ t = \left( 1 - \frac{1}{\mu} \right)t\]
\[ = \left( 1 - \frac{2}{3} \right)3\]
\[ = \left( \frac{1}{3} \right)3\]
\[ = 1 \text{ cm }\]
The upper surface of the paperweight is flat and the spherical spherical surface is in contact with the printed letter.
Therefore, we will take it as a simple refraction problem.
Hence, the image will appear 1 cm above point A.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
One day Chetan’s mother developed a severe stomach ache all of a sudden. She was rushed to the doctor who suggested for an immediate endoscopy test and gave an estimate of expenditure for the same. Chetan immediately contacted his class teacher and shared the information with her. The class teacher arranged for the money and rushed to the hospital. On realizing that Chetan belonged to a below average income group family, even the doctor offered concession for the test fee. The test was conducted successfully.
Answer the following questions based on the above information:
(a) Which principle in optics is made use of in endoscopy?
(b) Briefly explain the values reflected in the action taken by the teacher.
(c) In what way do you appreciate the response of the doctor on the given situation?
(a) A ray of monochromatic light enters glass PQRS as shown in the fig. Complete the path of ray till it emerges from the glass. (Critical angle of glass is 420).
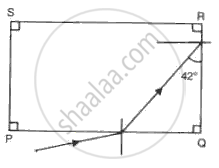
(b) Draw diagram of a prism periscope.
(c) What are the advantages of total internal reflecting prism over plane mirror?
State two advantages of using a right-angle prism as a reflector, rather than a plane mirror.
Images formed by totally reflecting prisms are brighter than the image formed by ordinary reflected light, why?
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
What is meant by the statement, ‘the critical angle for diamond is 24°’?
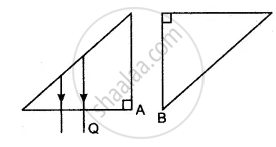
The adjacent diagram shows two right-angled isosceles prisms A and B. Complete the diagram to show the path of rays P and Q emerging out of the prism B. What principles have you used to complete the diagram?
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions are total internal reflection possible? Explain it with a suitable example.
Answer the following question.
Why is prism binoculars preferred over traditional binoculars? Describe its working in brief.
Solve Numerical example.
A monochromatic ray of light is incident at 37° on an equilateral prism of refractive index 3/2. Determine angle of emergence and angle of deviation. If angle of prism is adjustable, what should its value be for emergent rays to be just possible for the same angle of incidence?
A particle is projected such that the horizontal range and vertical height are equal. Then the angle of projection is :
Which of the following statements about total internal reflection is true?
What are the conditions to achieve total internal reflection?
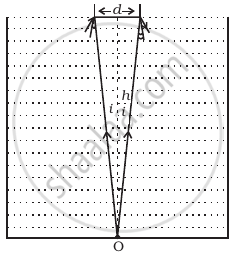
A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index µ (Figure). At the centre of the jar on the bottom surface is a dot. Find the minimum diameter of a disc, such that when placed on the top surface symmetrically about the centre, the dot is invisible.
Which of the following is used in optical fibres?
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index µ, the angle of incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. Then the angle of incidence is ______.
- Assertion (A): Propagation of light through an optical fibre is due to total internal reflection taking place at the core-cladding interface.
- Reason (R): Refractive index of the material of the cladding of the optical fibre is greater than that of the core.
Name any two phenomena which take place in the formation of a rainbow.
The diagram below shows a fish in the tank and its image seen in the surface of water.

Name the phenomenon responsible for the formation of this image.
