Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Describe the construction and working of an optical fibre.
Solution
Construction:
- An optical fibre consists of an extremely thin, transparent, and flexible core surrounded by an optically rarer flexible cover called cladding.
- For protection, the whole system is coated by a buffer and a jacket
- The entire thickness of the fibre is less than half an mm.
- Many such fibres can be packed together in an outer cover.

Construction of Optical fiber
Working:
- Working of optical fibre is based on the principle of total internal reflection.
- An optical signal (a ray of light) entering the core suffers multiple total internal reflections before emerging out after several kilometres.
- The optical signal travels with the highest possible speed in the material.
- The emerged optical signal has an extremely low loss in signal strength.
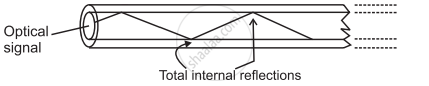
Working of Optical fibre
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
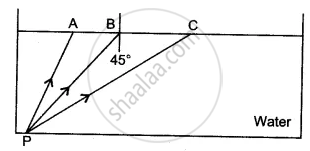
The diagram below shows a point source P inside a water container. Four rays A, B, C, D starting from the source P are shown up to the water surface
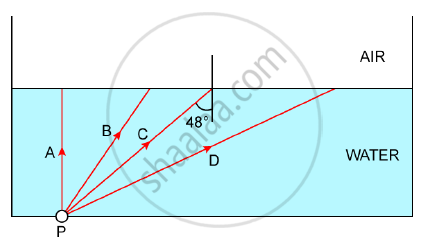
1) Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface.
The Critical Angle for the water-air surface is 48°.
2) Name the phenomenon which the rays B and D exhibit.
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism? Why is it caused?
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incident is ______.
Name two factors which affect the critical angle for a given pair of media. State how do the factors affect it.
In the given figure PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. The ray PQ is refracted as QS.
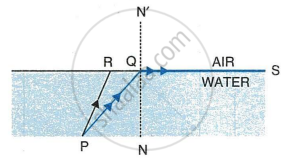
- State the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN of the ray PQ.
- What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
- Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
- The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason.
- Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P’ when seen vertically from above.
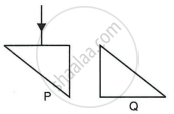
Two isosceles right-angle glass prisms P and Q are placed near each other as shown in Fig. Complete the path of the light ray entering the prism P till it emerges out of the prism Q.
One day Chetan’s mother developed a severe stomach ache all of a sudden. She was rushed to the doctor who suggested for an immediate endoscopy test and gave an estimate of expenditure for the same. Chetan immediately contacted his class teacher and shared the information with her. The class teacher arranged for the money and rushed to the hospital. On realizing that Chetan belonged to a below average income group family, even the doctor offered concession for the test fee. The test was conducted successfully.
Answer the following questions based on the above information:
(a) Which principle in optics is made use of in endoscopy?
(b) Briefly explain the values reflected in the action taken by the teacher.
(c) In what way do you appreciate the response of the doctor on the given situation?
Plot a graph between
Sine of angle of incidence versus sine of angle of refraction,
Make the correct choices for each of the following :
Total Internal reflection takes place when
(where ∠i = angle of incidence, ∠r = angle of refraction, ∠C = critical angle)
How does a ray of light bend when it travels from rarer to denser medium
Can light be ‘piped’ like sound in a doctor’s stethoscope?
Write down the relationship between the critical angle and the refractive index of the medium.
If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about the refractive indices of these media (angle I is not 0)?
What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
The diagram shows a point source P inside a water container. Three rays A, B, and C starting from P are shown up to the water surface. Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface. The critical angle for the water-air pair is 48°.
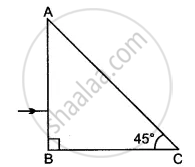
A ray of light passes through a right-angled prism as shown in the figure. State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
Answer the following question.
Why is prism binoculars preferred over traditional binoculars? Describe its working in brief.
Solve Numerical example.
From the given data set, determine angular dispersion by the prism and dispersive power of its material for extreme colours. nR = 1.62 nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
Total internal reflection can take place only if light is travelling from ______.
The entire light is reflected back into the denser medium is called ______.
The outer concentric shell in optic fiber is called ______.
A bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages using light waves is called ______.
Optical Fibres are based on the phenomenon of dispersion.
Write any two uses of total internal reflection.
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere is similar to ______.
Observe the given figure of the raindrop and answer the following questions:
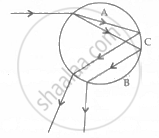
- Label A and B of the given diagram. Why colour will deviate most.
- Name the phenomenon shown in label C.
A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism P. Additional prism Q and R of identical shape and of the same material as P are now added as shown in the figure. The ray will now suffer ______.

Name any two phenomena which take place in the formation of a rainbow.
