Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Describe the construction and working of an optical fibre.
उत्तर
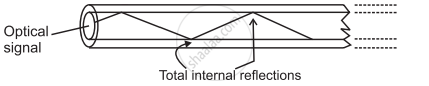
Construction:
- An optical fibre consists of an extremely thin, transparent, and flexible core surrounded by an optically rarer flexible cover called cladding.
- For protection, the whole system is coated by a buffer and a jacket
- The entire thickness of the fibre is less than half an mm.
- Many such fibres can be packed together in an outer cover.

Construction of Optical fiber
Working:
- Working of optical fibre is based on the principle of total internal reflection.
- An optical signal (a ray of light) entering the core suffers multiple total internal reflections before emerging out after several kilometres.
- The optical signal travels with the highest possible speed in the material.
- The emerged optical signal has an extremely low loss in signal strength.
Working of Optical fibre
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A ray of light travels from water to air as shown in the diagram given below :

1) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the way. Given the critical angle for water is 48°.
2) State the condition so that internal reflection occurs in the above diagram.
The diagram below shows a point source P inside a water container. Four rays A, B, C, D starting from the source P are shown up to the water surface
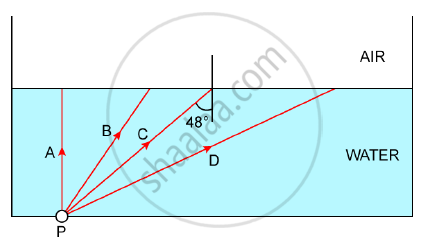
1) Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface.
The Critical Angle for the water-air surface is 48°.
2) Name the phenomenon which the rays B and D exhibit.
Which colour of light has a higher critical angle? Red light or green light.
Total internal reflection occurs only when a ray of light passes from a ______ medium to a ______ medium.
Calculate the speed of light in a medium whose critical angle is 30° ?
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of reflection,
If a light ray does not undergo, refraction at the boundary between two media, the angle of incidence is:
Name the principle on the basis of which optical fibres work.
Can light be ‘piped’ like sound in a doctor’s stethoscope?
How are critical angles related to the refractive index of the medium?
Images formed by totally reflecting prisms are brighter than the image formed by ordinary reflected light, why?
A ray of light incident at an angle of incidence ‘i’ passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to its base and emerges from the prism at an angle of emergence ‘e’.
What can you say about the value of the angle of deviation in such a situation?
What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
Draw a diagram, properly labelled, to illustrate the use of a total reflecting prism (a right-angled isosceles prism) to turn a ray of light through 180°. Name an instrument in which this device is used.
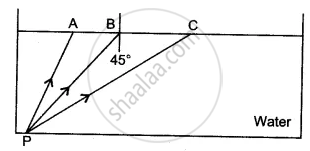
The diagram shows a point source P inside a water container. Three rays A, B, and C starting from P are shown up to the water surface. Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface. The critical angle for the water-air pair is 48°.
A spherical marble, of refractive index 1.5 and curvature 1.5 cm, contains a tiny air bubble at its centre. Where will it appear when seen from outside?
Answer the following question.
Define the critical angle of incidence and obtain an expression for it.
For the same angle of incidence, the angle of refraction in four media A, B, C and D are 25°, 30°, 35° and 40° respectively. The speed of light is least in medium ______.
For total internal reflection to take place, the angle of inddence i and the refractive index µ of the medium must satisfy the inequality ____________.
The angle of minimum deviation produced by a thin glass prism in air is 'δ'. If that prism is immersed in water, the angle of minimum deviation will be ______.
( aμg = refractive index of glass w.r.t, air aμw = refractive index of water w.r.t. air)
For a ray of light, the critical angle is minimum when it travels from ______.
A particle is projected such that the horizontal range and vertical height are equal. Then the angle of projection is :
A bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages using light waves is called ______.
What are the examples of total internal reflection in nature?
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle (θ). Select the correct statement.
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere is similar to ______.
A ray of light passes through a prism of refractive index `sqrt2` as shown in the figure. Find:
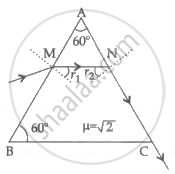
- The angle of incidence (∠r2) at face AC.
- The angle of minimum deviation for this prism.
The angle made by incident ray of light with normal of the reflecting surface is called ______.
- Assertion (A): Propagation of light through an optical fibre is due to total internal reflection taking place at the core-cladding interface.
- Reason (R): Refractive index of the material of the cladding of the optical fibre is greater than that of the core.
