Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere is similar to ______.
पर्याय
reflection of light by a plane mirror.
total internal reflection of light in air during a mirage.
dispersion of light by water molecules during the formation of a rainbow.
scattering of light by the particles of air.
उत्तर
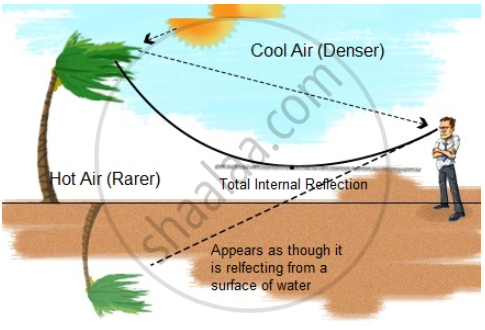
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere is similar to total internal reflection of light in air during a mirage.
Explanation:
Radio waves are reflected by a layer of the atmosphere called the Ionosphere, so they can reach distant parts of the Earth. The reflection of radio waves by ionosphere is due to total internal reflection. It is the same as total internal reflection of light in the air during a mirage, i.e., angle of incidence is greater than critical angle.
Important point: The ionized part of the Earth’s atmosphere is known as the ionosphere. Ultraviolet light from the sun collides with atoms in this region knocking electrons loose. The creates ions or atoms with missing electrons. This is what gives the Ionosphere its name- and it is the free electrons that cause the reflection and absorption of ratio waves.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of refraction.
Make the correct choices for each of the following :
Total Internal reflection takes place when
(where ∠i = angle of incidence, ∠r = angle of refraction, ∠C = critical angle)
A ray of light is incident on a glass surface at an angle of 50° with the corresponding angle of refraction 30°. Find the value of the R.I. of glass.
A spherical marble, of refractive index 1.5 and curvature 1.5 cm, contains a tiny air bubble at its centre. Where will it appear when seen from outside?
Choose the correct option.
Select the WRONG statement.
Optical fibre communication uses the principle of ______.
The outer concentric shell in optic fiber is called ______.
What is a mirage? How does it occur?
What is the phenomenon used in optical fiber? Explain.
