Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
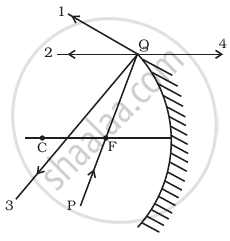
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
पर्याय
1
2
3
4
उत्तर
2
Explanation:
The ray PQ of light passes through focus F and incident on the concave mirror, after reflection, should become parallel to the principal axis as shown by ray 2 in the figure.
Important points: We can locate the image of any extended object graphically by drawing any two of the following four special rays:
- A ray initially parallel to the principal axis is reflected through the focus of the mirror (1).
- A ray passing through the center of curvature is reflected back along itself (3).
- A ray initially passing through the focus is reflected parallel to the principal axis (2).
- A ray incident at the pole is reflected symmetrically.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
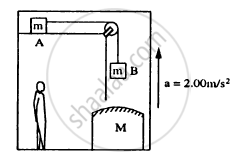
Consider the situation shown in figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration of 2.00 m s−2 and the focal length of the mirror is 12.0 cm. All the surfaces are smooth and the pulley is light. The mass-pulley system is released from rest (with respect to the elevator) at t = 0 when the distance of B from the mirror is 42.0 cm. Find the distance between the image of the block B and the mirror at t = 0.200 s. Take g = 10 m s−2.
Answer the following question.
Three lenses of focal length +10 cm, —10 cm and +30 cm are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.

Answer the following question.
With the help of a ray diagram, obtain the relation between its focal length and radius of curvature.
According to the mirror equation, ______.
An object is 20 cm away from a concave mirror and it is within the focal length of the mirror. If the mirror is changed to a plane mirror, the image moves 15 cm closer to the mirror.
Focal length of the concave mirror is ______.
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm forms three times the magnified virtual image of an object. Find the distance of the object from the mirror.
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
