Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
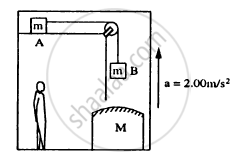
Consider the situation shown in figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration of 2.00 m s−2 and the focal length of the mirror is 12.0 cm. All the surfaces are smooth and the pulley is light. The mass-pulley system is released from rest (with respect to the elevator) at t = 0 when the distance of B from the mirror is 42.0 cm. Find the distance between the image of the block B and the mirror at t = 0.200 s. Take g = 10 m s−2.
उत्तर
Given,
Acceleration of the elevator, a = 2.00 m/s2
Focal length of the mirror M, f = 12.00 cm
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2
Mass of blocks A and B = m
As per the question, the mass–pulley system is released at time t = 0.
Let the acceleration of the masses A and B with respect to the elevator be a.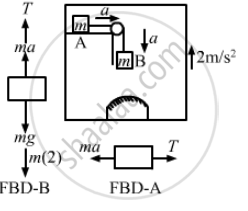
Using the free body diagram,
T − mg + ma − 2m = 0 ...(i)
Also,
T − ma = 0 ...(ii)
From (i) and (ii), we get:
2ma = m(g + 2)
`⇒ a = (10 + 2)/2`
`= 12/2 = 6 ms^-2`
Now, the distance travelled by block B of mass m in time t = 0.2 s is given by
`s = ut + 1/2at^2`
As `(u = 0)`
`s = 1/2 at^2`
On putting the respective values, we get:
`s = 1/2 xx 6 xx (0.2)^2`
`= 0.12 m = 12 cm`
As given in the question, the distance of block B from the mirror is 42 cm.
Object distance u from the mirror = − (42 − 12) = − 30 cm Using the mirror equation,
`1/v + 1/u = 1/f`
On putting the respective values, we get:
`1/v + 1/-30 = 1/12`
⇒ `1/v= 1/-30 = 1/ 12 + 1/30`
⇒ `v = 8.57 cm `
Hence, the distance between block B and mirror M is 8.57 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
Can mirrors give rise to chromatic aberration?
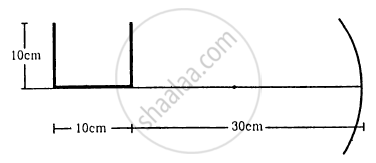
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature 20 cm as shown in figure. Find the total length of the image.
A diverging lens of focal length 20 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed coaxially at a separation of 5 cm. Where should an object be placed so that a real image is formed at the object itself?
A converging lens of focal length 12 cm and a diverging mirror of focal length 7.5 cm are placed 5.0 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed so that its image falls on itself?
A converging lens and a diverging mirror are placed at a separation of 15 cm. The focal length of the lens is 25 cm and that of the mirror is 40 cm. Where should a point source be placed between the lens and the mirror so that the light, after getting reflected by the mirror and then getting transmitted by the lens, comes out parallel to the principal axis?
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30 cm. Find the focal length of the combination .
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
Answer the following question.
With the help of a ray diagram, obtain the relation between its focal length and radius of curvature.
Focal length of a mirror is given by ______.
A thin converging lens of focal length 12 cm is kept in contact with a thin diverging lens of focal length 18 cm. Calculate the effective/equivalent focal length of the combination.
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will ______.
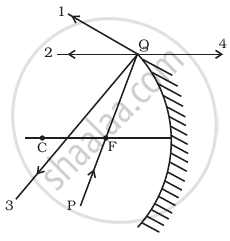
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
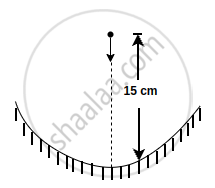
A particle is dropped along the axis from a height 15 cm on a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm as shown in figure. The acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2. Find the maximum speed of image in m/s:
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
