Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
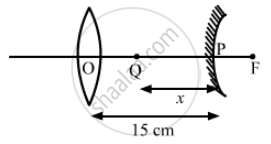
A converging lens and a diverging mirror are placed at a separation of 15 cm. The focal length of the lens is 25 cm and that of the mirror is 40 cm. Where should a point source be placed between the lens and the mirror so that the light, after getting reflected by the mirror and then getting transmitted by the lens, comes out parallel to the principal axis?
उत्तर
Given,
Distance between the convex lens and the convex mirror is 15 cm.
The focal length (f1) of the lens is 25 cm.
The focal length (f2) of the mirror is 40 cm.
Let x cm be the object distance from the mirror.
Therefore,
u = − x cm
v = 25 − 15 = + 10 cm (∵ focal length of lens = 25 cm)
∴ f1 = + 40 cm
Using lens formula:
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\Rightarrow\frac{1}{x}=\frac{1}{10}-\frac{1}{40}\Rightarrow x=\frac{400}{30} = \frac{40}{3}\]
Thus, the object distance is \[\left( 15 - \frac{40}{3} \right)=\frac{5}{3}\]
= 1.67 cm from the lens
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
(a) the object and the image are both real
(b) the object and the image are both virtual
(c) the object is real but the image is virtual
(d) the object is virtual but the image is real.
A spherical surface of radius 30 cm separates two transparent media A and B with refractive indices 1.33 and 1.48 respectively. The medium A is on the convex side of the surface. Where should a point object be placed in medium A so that the paraxial rays become parallel after refraction at the surface?
A narrow pencil of parallel light is incident normally on a solid transparent sphere of radius r. What should be the refractive index is the pencil is to be focussed (a) at the surface of the sphere, (b) at the centre of the sphere.
A converging lens of focal length 12 cm and a diverging mirror of focal length 7.5 cm are placed 5.0 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed so that its image falls on itself?
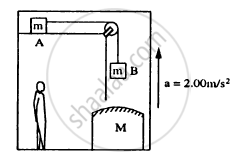
Consider the situation shown in figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration of 2.00 m s−2 and the focal length of the mirror is 12.0 cm. All the surfaces are smooth and the pulley is light. The mass-pulley system is released from rest (with respect to the elevator) at t = 0 when the distance of B from the mirror is 42.0 cm. Find the distance between the image of the block B and the mirror at t = 0.200 s. Take g = 10 m s−2.
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30 cm. Find the focal length of the combination .
State how the focal length of a glass lens (Refractive Index 1.5) changes when it is completely immersed in:
(i) Water (Refractive Index 1.33)
(ii) A liquid (Refractive Index 1.65)
Focal length of a mirror is given by ______.
The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25?
Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
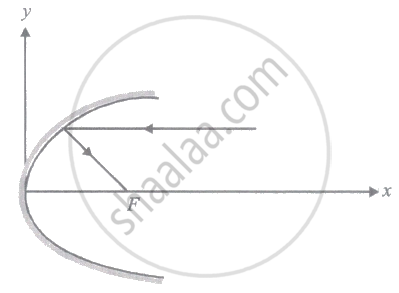
A parallel beam of light ray parallel to the x-axis is incident on a parabolic reflecting surface x = 2by2 as shown in the figure. After reflecting it passes through focal point F. What is the focal length of the reflecting surface?
A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror away from focus. The object distance is u. If the mirror has a focal length f, what will be the length of the image? You may take L << |v – f|.
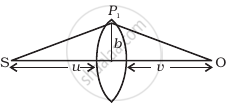
(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Figure). Let the thickness of the lens vary as `w(b) = w_0 - b^2/α`, where b is the verticle distance from the pole. `w_0` is a constant. Using Fermat’s principle i.e. the time of transit for a ray between the source and observer is an extremum, find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.
(ii) A gravitational lens may be assumed to have a varying width of the form
`w(b) = k_1ln(k_2/b) b_("min") < b < b_("max")`
= `k_1ln (K_2/b_("min")) b < b_("min")`
Show that an observer will see an image of a point object as a ring about the center of the lens with an angular radius
`β = sqrt((n - 1)k_1 u/v)/(u + v)`
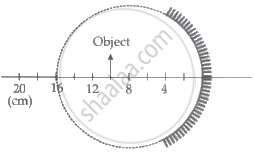
A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the figure from a hollow glass sphere. if an object is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be the nature and magnification of the image of the object? (Figure drawn as schematic and not to scale)
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm forms three times the magnified virtual image of an object. Find the distance of the object from the mirror.
A converging lens has a focal length of 10 cm in air. It is made of a material with a refractive index of 1.6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.3, find its new focal length.
If an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 20 cm, the image formed will be ______.
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
