Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 20 cm, the image formed will be ______.
पर्याय
Real and 20 cm in front of the mirror
Real and 6.67 cm in front of the mirror.
Virtual and 20 cm behind the mirror.
Virtual and 6.67 cm behind the mirror.
उत्तर
If an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 20 cm, the image formed will be virtual and 20 cm behind the mirror.
Explanation:
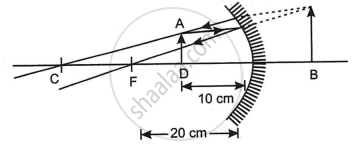
Given, f = - 20 cm; u = - 10 cm
Using the formula
`1/"f" = 1/"v" + 1/"u"`
`=> 1/(- 20) = 1/v - 1/10`
`=> 1/10 - 1/20 = 1/v`
`=> 1/v = 1/20`
⇒ v = 20 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
If an object far away from a convex mirror moves towards the mirror, the image also moves. Does it move faster, slower or at the same speed as compared to the object?
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
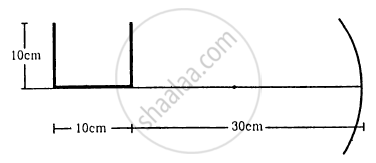
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature 20 cm as shown in figure. Find the total length of the image.
State how the focal length of a glass lens (Refractive Index 1.5) changes when it is completely immersed in:
(i) Water (Refractive Index 1.33)
(ii) A liquid (Refractive Index 1.65)
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will ______.
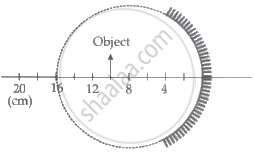
A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the figure from a hollow glass sphere. if an object is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be the nature and magnification of the image of the object? (Figure drawn as schematic and not to scale)
An object is 20 cm away from a concave mirror and it is within the focal length of the mirror. If the mirror is changed to a plane mirror, the image moves 15 cm closer to the mirror.
Focal length of the concave mirror is ______.
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
