Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If an object far away from a convex mirror moves towards the mirror, the image also moves. Does it move faster, slower or at the same speed as compared to the object?
उत्तर
The image of the object moves slower compared to the object. It can be explained using the mirror formula :
\[\frac{1}{u} + \frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{f}\]
We know that for a convex mirror, the object distance (u) is positive, image distance (v) is negative and the focal length (f) is also negative. Thus mirror formula of a convex mirror is:
\[\frac{1}{u} - \frac{1}{v} = - \frac{1}{f}\]
As u = +ve
\[\frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{f} > 0\]
\[\frac{1}{v} > \frac{1}{f}\]
\[v < f\]
Therefore, the image is always formed within the focal length of the mirror. Thus, the distance moved by the image is much slower than the distance moved by the object.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
Can mirrors give rise to chromatic aberration?
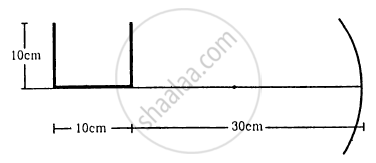
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature 20 cm as shown in figure. Find the total length of the image.
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Sketch the variation of the angle of deviation δ with the angle of incident i for 0 < i < 90°.
A diverging lens of focal length 20 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed coaxially at a separation of 5 cm. Where should an object be placed so that a real image is formed at the object itself?
A converging lens of focal length 12 cm and a diverging mirror of focal length 7.5 cm are placed 5.0 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed so that its image falls on itself?
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30 cm. Find the focal length of the combination .
How can the spherical aberration produced by a lens be minimized?
According to Cartesian sign convention, all distances are measured from the _______.
A thin converging lens of focal length 12 cm is kept in contact with a thin diverging lens of focal length 18 cm. Calculate the effective/equivalent focal length of the combination.
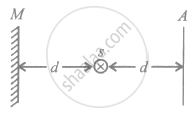
The intensity of a point source of light, S, placed at a distance d in front of a screen A, is I0 at the center of the screen. Find the light intensity at the center of the screen if a completely reflecting plane mirror M is placed at a distance d behind the source, as shown in the figure.
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will ______.
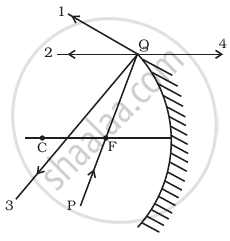
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length 20 m and an eyepiece of focal length 2 cm.
- The length of the telescope tube is 20.02 m.
- The magnification is 1000.
- The image formed is inverted.
- An objective of a larger aperture will increase the brightness and reduce chromatic aberration of the image.
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
