Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Sketch the variation of the angle of deviation δ with the angle of incident i for 0 < i < 90°.
उत्तर
Given,
Refractive index of glass, μg = 1.5
Refractive index of air, μa= 1.0
Angle of incidence 0° < i < 90
Let us take θc as the Critical angle
\[\Rightarrow \frac{\sin \theta c}{\sin r} = \frac{\mu_a}{\mu_g}\]
\[\Rightarrow \frac{\sin \theta_c}{\sin 90^\circ } = \frac{1}{1 . 5} = 0 . 66\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta_c = 0 . 66\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta_c = \sin {}^{- 1} \left( 0 . 66 \right)\]
⇒ θc = 40°48"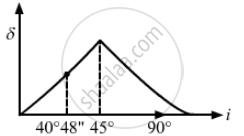
The angle of deviation (δ) due to refraction from glass to air increases as the angle of incidence increases from 0° to 40°48". The angle of deviation (δ) due to total internal reflection further increases from 40°48" to 45° and then it decreases, as shown in the graph.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
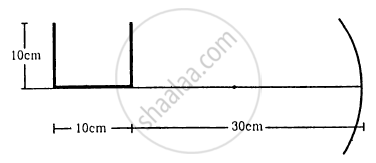
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature 20 cm as shown in figure. Find the total length of the image.
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
(a) the object and the image are both real
(b) the object and the image are both virtual
(c) the object is real but the image is virtual
(d) the object is virtual but the image is real.
A diverging lens of focal length 20 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed coaxially at a separation of 5 cm. Where should an object be placed so that a real image is formed at the object itself?
A converging lens and a diverging mirror are placed at a separation of 15 cm. The focal length of the lens is 25 cm and that of the mirror is 40 cm. Where should a point source be placed between the lens and the mirror so that the light, after getting reflected by the mirror and then getting transmitted by the lens, comes out parallel to the principal axis?
How can the spherical aberration produced by a lens be minimized?
State how the focal length of a glass lens (Refractive Index 1.5) changes when it is completely immersed in:
(i) Water (Refractive Index 1.33)
(ii) A liquid (Refractive Index 1.65)
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
Answer the following question.
With the help of a ray diagram, obtain the relation between its focal length and radius of curvature.
According to Cartesian sign convention, all distances are measured from the _______.
According to the mirror equation, ______.
A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h–1 on a straight road. Looking at the rear view mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h–1. In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 s till the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm above the principal axis. The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object placed at (– 50 cm, 0). Find the coordinates of the image.
An object is 20 cm away from a concave mirror and it is within the focal length of the mirror. If the mirror is changed to a plane mirror, the image moves 15 cm closer to the mirror.
Focal length of the concave mirror is ______.
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm forms three times the magnified virtual image of an object. Find the distance of the object from the mirror.
A converging lens has a focal length of 10 cm in air. It is made of a material with a refractive index of 1.6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.3, find its new focal length.
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
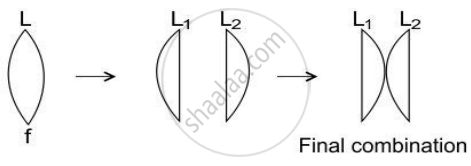
A lens of focal length f is divided into two equal parts and then these parts are put in a combination as shown in the figure below.
- What is the focal length of L1?
- What is the focal length of the final combination?