Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm above the principal axis. The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object placed at (– 50 cm, 0). Find the coordinates of the image.
उत्तर
If a symmetric lens is cut parallel to principal axis in two parts. The focal length remains the same for each part. The intensity of image formed by each part will be less compared to that of the complete lens.
If there was no cut, then the object would been at a height of 0.5 cm from the principal axis O'.
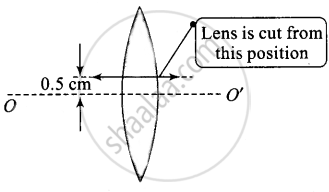
The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object is placed at (– 50 cm, 0). There is no effect on the focal length of the lens.
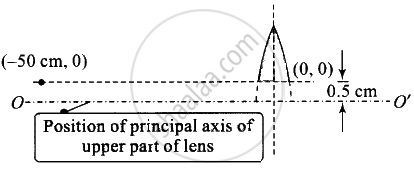
u = – 50 cm, f = 25 cm, v = ?
`1/v - 1/u = 1/f`
`1/v - 1/(-50) = 1/25`
`1/v = 1/25 - 1/50`
= `(2 - 1)/50 = 1/50`
v = 50 cm
`m = (+v)/u = (+(50))/(-50)` = – 1
So the size of image is equal to that of object, m is negative so image is inverted.
So image is at (50 cm), – 1 cm) and 0.5 cm below the X – x' axis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
If an object far away from a convex mirror moves towards the mirror, the image also moves. Does it move faster, slower or at the same speed as compared to the object?
A converging lens of focal length 12 cm and a diverging mirror of focal length 7.5 cm are placed 5.0 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed so that its image falls on itself?
State how the focal length of a glass lens (Refractive Index 1.5) changes when it is completely immersed in:
(i) Water (Refractive Index 1.33)
(ii) A liquid (Refractive Index 1.65)
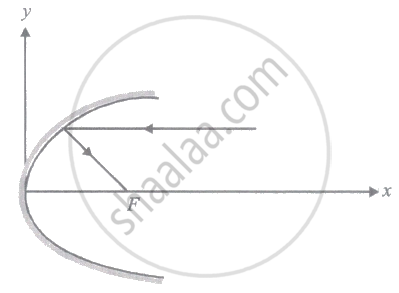
A parallel beam of light ray parallel to the x-axis is incident on a parabolic reflecting surface x = 2by2 as shown in the figure. After reflecting it passes through focal point F. What is the focal length of the reflecting surface?
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
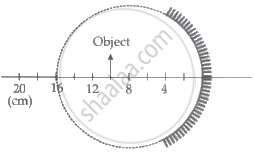
A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the figure from a hollow glass sphere. if an object is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be the nature and magnification of the image of the object? (Figure drawn as schematic and not to scale)
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
