Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm above the principal axis. The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object placed at (– 50 cm, 0). Find the coordinates of the image.
उत्तर
If a symmetric lens is cut parallel to principal axis in two parts. The focal length remains the same for each part. The intensity of image formed by each part will be less compared to that of the complete lens.
If there was no cut, then the object would been at a height of 0.5 cm from the principal axis O'.
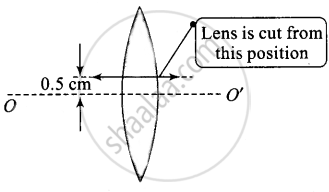
The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object is placed at (– 50 cm, 0). There is no effect on the focal length of the lens.
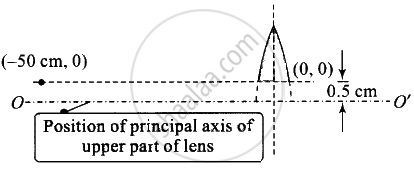
u = – 50 cm, f = 25 cm, v = ?
`1/v - 1/u = 1/f`
`1/v - 1/(-50) = 1/25`
`1/v = 1/25 - 1/50`
= `(2 - 1)/50 = 1/50`
v = 50 cm
`m = (+v)/u = (+(50))/(-50)` = – 1
So the size of image is equal to that of object, m is negative so image is inverted.
So image is at (50 cm), – 1 cm) and 0.5 cm below the X – x' axis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
A man uses a concave mirror for shaving. He keeps his face at a distance of 25 cm from the mirror and gets an image which is 1.4 times enlarged. Find the focal length of the mirror.
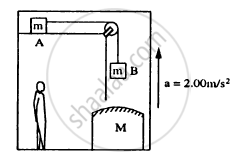
Consider the situation shown in figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration of 2.00 m s−2 and the focal length of the mirror is 12.0 cm. All the surfaces are smooth and the pulley is light. The mass-pulley system is released from rest (with respect to the elevator) at t = 0 when the distance of B from the mirror is 42.0 cm. Find the distance between the image of the block B and the mirror at t = 0.200 s. Take g = 10 m s−2.
According to the mirror equation, ______.
A thin converging lens of focal length 12 cm is kept in contact with a thin diverging lens of focal length 18 cm. Calculate the effective/equivalent focal length of the combination.
The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25?
Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
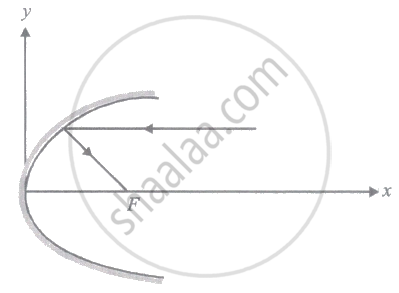
A parallel beam of light ray parallel to the x-axis is incident on a parabolic reflecting surface x = 2by2 as shown in the figure. After reflecting it passes through focal point F. What is the focal length of the reflecting surface?
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
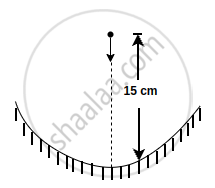
A particle is dropped along the axis from a height 15 cm on a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm as shown in figure. The acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2. Find the maximum speed of image in m/s: