Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
विकल्प
The beam of red light would undergo total internal reflection.
The beam of red light would bend towards normal while it gets refracted through the second medium.
The beam of blue light would undergo total internal reflection.
The beam of green light would bend away from the normal as it gets refracted through the second medium.
उत्तर
The beam of blue light would undergo total internal reflection.
Explanation:
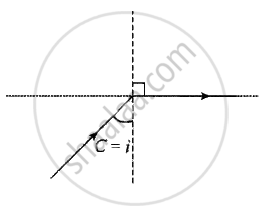
According to the Cauchy relationship, `lambda oo 1/mu`
Smaller the wavelength higher the refractive index and consequently smaller the critical angle.
We know `v = flambda`, the frequency of wave remains unchanged with medium hence `v oo lambda`.
The critical angle, sin C = `1/mu`
Also, velocity of light, `v oo 1/mu`
According to VIBGYOR, among all given sources of light, the blue light have smallest wavelength, As `lambda_("blu") < lambda_("yellow")` hence `v_("blue") < v_("yellow")`, it means `mu_("blue") > mu_("yellow")`
It means critical angle for blue is less than yellow colour, the critical angle is least which facilitates total internal reflection for the beam of blue light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
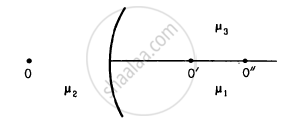
Following figure shows three transparent media of refractive indices \[\mu_1 , \mu_2 \text{ and } \mu_3\]. A point object O is placed in the medium \[\mu_2\]. If the entire medium on the right of the spherical surface has refractive index \[\mu_3\], the image forms at O". In the situation shown,
A spherical surface of radius 30 cm separates two transparent media A and B with refractive indices 1.33 and 1.48 respectively. The medium A is on the convex side of the surface. Where should a point object be placed in medium A so that the paraxial rays become parallel after refraction at the surface?
A diverging lens of focal length 20 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed coaxially at a separation of 5 cm. Where should an object be placed so that a real image is formed at the object itself?
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30 cm. Find the focal length of the combination .
How can the spherical aberration produced by a lens be minimized?
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
A thin converging lens of focal length 12 cm is kept in contact with a thin diverging lens of focal length 18 cm. Calculate the effective/equivalent focal length of the combination.
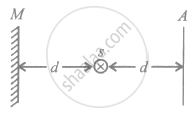
The intensity of a point source of light, S, placed at a distance d in front of a screen A, is I0 at the center of the screen. Find the light intensity at the center of the screen if a completely reflecting plane mirror M is placed at a distance d behind the source, as shown in the figure.
A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm above the principal axis. The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object placed at (– 50 cm, 0). Find the coordinates of the image.
