Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will ______.
विकल्प
act as a convex lens only for the objects that lie on its curved side.
act as a concave lens for the objects that lie on its curved side.
act as a convex lens irrespective of the side on which the object lies.
act as a concave lens irrespective of side on which the object lies.
उत्तर
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will act as a convex lens irrespective of the side on which the object lies.
Explanation:
If object lies on curved side then R1 = +20 cm and R2 = `oo`, μ1 = 1, μ2 = 1.5
`1/f = (mu_2 - mu_1) (1/R_1 - 1/R_2)`
`1/f = (1.5 - 1) (1/20 - 1/oo) = 0.5/20 = 5/200 = 1/40`
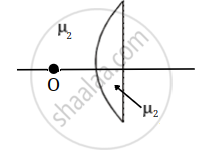
F = + 40 cm
If object lies on plane side R1 = `oo` and R2 = – 20 cm, μ1 = 1, μ2 = 1.5
`1/f = (mu_2 - mu_1) (1/R_1-1/R_2)`
`1/f = (1.5 - 1)(1/oo - (- 1/20)) = 0.5 xx (+ 1/20)`
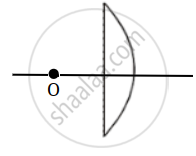
`1/f = 5/200`
f = + 40 cm
So, lens will always act as a convex lens irrespective of the side on which objects lie.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
Can mirrors give rise to chromatic aberration?
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
(a) the object and the image are both real
(b) the object and the image are both virtual
(c) the object is real but the image is virtual
(d) the object is virtual but the image is real.
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30 cm. Find the focal length of the combination .
Two thin lenses having optical powers of -10D and+ 6D are placed in contact with each other. The focal length of the combination is:
Focal length of a mirror is given by ______.
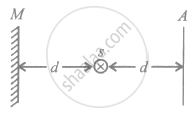
The intensity of a point source of light, S, placed at a distance d in front of a screen A, is I0 at the center of the screen. Find the light intensity at the center of the screen if a completely reflecting plane mirror M is placed at a distance d behind the source, as shown in the figure.
A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm above the principal axis. The top part is placed at (0, 0) and an object placed at (– 50 cm, 0). Find the coordinates of the image.
A converging lens has a focal length of 10 cm in air. It is made of a material with a refractive index of 1.6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.3, find its new focal length.
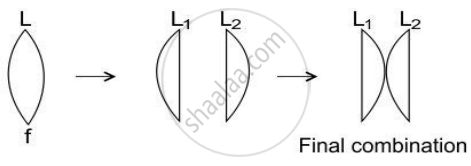
A lens of focal length f is divided into two equal parts and then these parts are put in a combination as shown in the figure below.
- What is the focal length of L1?
- What is the focal length of the final combination?