Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30 cm. Find the focal length of the combination .
उत्तर
`1/(F') = 1/(f_1) + 1/(f_2) = 1/(+40) +1/(-30) =1/40 - 1/30`
`1/(F') = (3-47)/120 = 1/120 `cm [Diverging]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
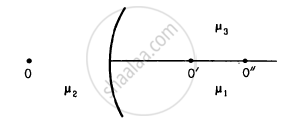
Following figure shows three transparent media of refractive indices \[\mu_1 , \mu_2 \text{ and } \mu_3\]. A point object O is placed in the medium \[\mu_2\]. If the entire medium on the right of the spherical surface has refractive index \[\mu_3\], the image forms at O". In the situation shown,
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Sketch the variation of the angle of deviation δ with the angle of incident i for 0 < i < 90°.
A spherical surface of radius 30 cm separates two transparent media A and B with refractive indices 1.33 and 1.48 respectively. The medium A is on the convex side of the surface. Where should a point object be placed in medium A so that the paraxial rays become parallel after refraction at the surface?
Answer the following question.
Three lenses of focal length +10 cm, —10 cm and +30 cm are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.

According to Cartesian sign convention, all distances are measured from the _______.
A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h–1 on a straight road. Looking at the rear view mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h–1. In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 s till the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
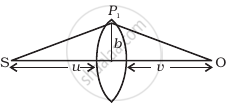
(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Figure). Let the thickness of the lens vary as `w(b) = w_0 - b^2/α`, where b is the verticle distance from the pole. `w_0` is a constant. Using Fermat’s principle i.e. the time of transit for a ray between the source and observer is an extremum, find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.
(ii) A gravitational lens may be assumed to have a varying width of the form
`w(b) = k_1ln(k_2/b) b_("min") < b < b_("max")`
= `k_1ln (K_2/b_("min")) b < b_("min")`
Show that an observer will see an image of a point object as a ring about the center of the lens with an angular radius
`β = sqrt((n - 1)k_1 u/v)/(u + v)`
An object is 20 cm away from a concave mirror and it is within the focal length of the mirror. If the mirror is changed to a plane mirror, the image moves 15 cm closer to the mirror.
Focal length of the concave mirror is ______.
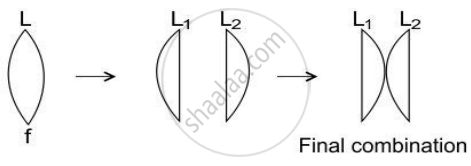
A lens of focal length f is divided into two equal parts and then these parts are put in a combination as shown in the figure below.
- What is the focal length of L1?
- What is the focal length of the final combination?