Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h–1 on a straight road. Looking at the rear view mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h–1. In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 s till the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
विकल्प
The speed of the car in the rear is 65 km h–1.
In the side mirror the car in the rear would appear to approach with a speed of 5 km h–1 to the driver of the leading car.
In the rear view mirror the speed of the approaching car would appear to decrease as the distance between the cars decreases.
In the side mirror, the speed of the approaching car would appear to increase as the distance between the cars decreases.
उत्तर
In the side mirror, the speed of the approaching car would appear to increase as the distance between the cars decreases.
Explanation:
Object moving along the principal axis: On differentiating the mirror formula with respect to time, we get `(dv)/(dt) = - (v/u)^2 (du)/(dt) = - (f/(u - f))^2. (du)/(dt)`. where `(dv)/(dt)` is the velocity of image along the principal axis and `(du)/(dt)` is the velocity of object along the principal axis. A negative sign implies that the image, in case of mirror, always moves in the direction opposite to that of the object.
As the distance between the cars decreases, the speed of the image of the car would appear to increase.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
A spherical surface of radius 30 cm separates two transparent media A and B with refractive indices 1.33 and 1.48 respectively. The medium A is on the convex side of the surface. Where should a point object be placed in medium A so that the paraxial rays become parallel after refraction at the surface?
Answer the following question.
Three lenses of focal length +10 cm, —10 cm and +30 cm are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.

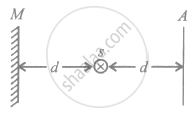
The intensity of a point source of light, S, placed at a distance d in front of a screen A, is I0 at the center of the screen. Find the light intensity at the center of the screen if a completely reflecting plane mirror M is placed at a distance d behind the source, as shown in the figure.
(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Figure). Let the thickness of the lens vary as `w(b) = w_0 - b^2/α`, where b is the verticle distance from the pole. `w_0` is a constant. Using Fermat’s principle i.e. the time of transit for a ray between the source and observer is an extremum, find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.
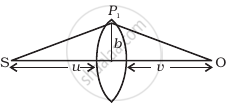
(ii) A gravitational lens may be assumed to have a varying width of the form
`w(b) = k_1ln(k_2/b) b_("min") < b < b_("max")`
= `k_1ln (K_2/b_("min")) b < b_("min")`
Show that an observer will see an image of a point object as a ring about the center of the lens with an angular radius
`β = sqrt((n - 1)k_1 u/v)/(u + v)`
Parallel rays striking a spherical mirror far from the optic axis are focussed at a different point than are rays near the axis thereby the focus moves toward the mirror as the parallel rays move toward the outer edge of the mirror. What value of incidence angle θ produces a 2% change in the location of the focus, compared to the location for θ very close to zero?
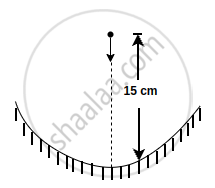
A particle is dropped along the axis from a height 15 cm on a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm as shown in figure. The acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2. Find the maximum speed of image in m/s:
A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm forms three times the magnified virtual image of an object. Find the distance of the object from the mirror.
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
