Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
उत्तर
Total Internal Reflection:
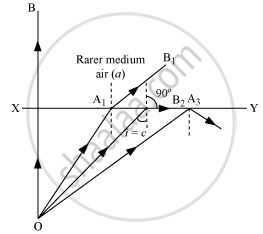
Total internal reflection is the phenomenon of reflection of light into a denser medium from an interface of the denser medium and the rarer medium. Two essential conditions for total internal reflection: Incident ray should travel in the denser medium and refracted ray should travel in the rarer medium.
The angle of incidence (i) should be greater than the critical angle for the pair of media in contact.
The relation between refractive index and critical angle (C):
When i = C and r = 90°
Apply Snell's law
`mu_b sinC = mu_a sin90^circ = mu_a xx 1`
`mu_b/mu_a = 1/sin C`
`""^amu_b = 1/sin C`.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.
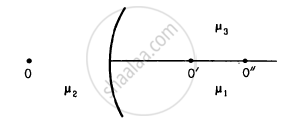
Following figure shows three transparent media of refractive indices \[\mu_1 , \mu_2 \text{ and } \mu_3\]. A point object O is placed in the medium \[\mu_2\]. If the entire medium on the right of the spherical surface has refractive index \[\mu_3\], the image forms at O". In the situation shown,
A converging lens of focal length 40 cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length 30 cm. Find the focal length of the combination .
Answer the following question.
Three lenses of focal length +10 cm, —10 cm and +30 cm are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.

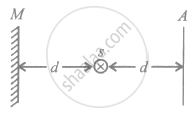
The intensity of a point source of light, S, placed at a distance d in front of a screen A, is I0 at the center of the screen. Find the light intensity at the center of the screen if a completely reflecting plane mirror M is placed at a distance d behind the source, as shown in the figure.
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
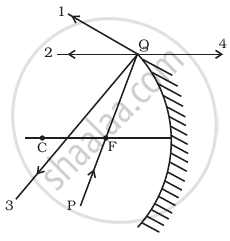
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror away from focus. The object distance is u. If the mirror has a focal length f, what will be the length of the image? You may take L << |v – f|.
An object is 20 cm away from a concave mirror and it is within the focal length of the mirror. If the mirror is changed to a plane mirror, the image moves 15 cm closer to the mirror.
Focal length of the concave mirror is ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm forms three times the magnified virtual image of an object. Find the distance of the object from the mirror.
