Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
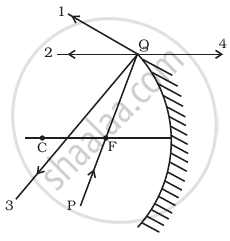
विकल्प
1
2
3
4
उत्तर
2
Explanation:
The ray PQ of light passes through focus F and incident on the concave mirror, after reflection, should become parallel to the principal axis as shown by ray 2 in the figure.
Important points: We can locate the image of any extended object graphically by drawing any two of the following four special rays:
- A ray initially parallel to the principal axis is reflected through the focus of the mirror (1).
- A ray passing through the center of curvature is reflected back along itself (3).
- A ray initially passing through the focus is reflected parallel to the principal axis (2).
- A ray incident at the pole is reflected symmetrically.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Sketch the variation of the angle of deviation δ with the angle of incident i for 0 < i < 90°.
A converging lens of focal length 12 cm and a diverging mirror of focal length 7.5 cm are placed 5.0 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed so that its image falls on itself?
Answer the following question.
Three lenses of focal length +10 cm, —10 cm and +30 cm are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.

Focal length of a mirror is given by ______.
The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25?
Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h–1 on a straight road. Looking at the rear view mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h–1. In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 s till the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the figure from a hollow glass sphere. if an object is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be the nature and magnification of the image of the object? (Figure drawn as schematic and not to scale)
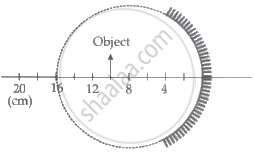
A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm forms three times the magnified virtual image of an object. Find the distance of the object from the mirror.
