Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
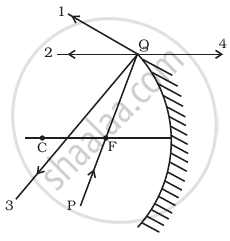
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (figure). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
Options
1
2
3
4
Solution
2
Explanation:
The ray PQ of light passes through focus F and incident on the concave mirror, after reflection, should become parallel to the principal axis as shown by ray 2 in the figure.
Important points: We can locate the image of any extended object graphically by drawing any two of the following four special rays:
- A ray initially parallel to the principal axis is reflected through the focus of the mirror (1).
- A ray passing through the center of curvature is reflected back along itself (3).
- A ray initially passing through the focus is reflected parallel to the principal axis (2).
- A ray incident at the pole is reflected symmetrically.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
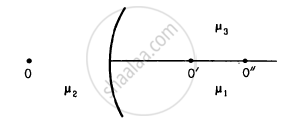
Following figure shows three transparent media of refractive indices \[\mu_1 , \mu_2 \text{ and } \mu_3\]. A point object O is placed in the medium \[\mu_2\]. If the entire medium on the right of the spherical surface has refractive index \[\mu_3\], the image forms at O". In the situation shown,
A man uses a concave mirror for shaving. He keeps his face at a distance of 25 cm from the mirror and gets an image which is 1.4 times enlarged. Find the focal length of the mirror.
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
(a) the object and the image are both real
(b) the object and the image are both virtual
(c) the object is real but the image is virtual
(d) the object is virtual but the image is real.
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Sketch the variation of the angle of deviation δ with the angle of incident i for 0 < i < 90°.
Two thin lenses having optical powers of -10D and+ 6D are placed in contact with each other. The focal length of the combination is:
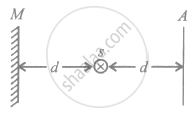
The intensity of a point source of light, S, placed at a distance d in front of a screen A, is I0 at the center of the screen. Find the light intensity at the center of the screen if a completely reflecting plane mirror M is placed at a distance d behind the source, as shown in the figure.
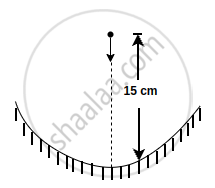
A particle is dropped along the axis from a height 15 cm on a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm as shown in figure. The acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2. Find the maximum speed of image in m/s:
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
