Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?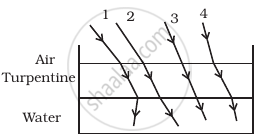
Options
1
2
3
4
Solution
2
Explanation:
Here, light ray goes from (optically) rarer medium air to optically denser medium turpentine, then it bends towards the normal, i.e., θ1 > θ2 whereas when it goes from optically denser medium turpentine to rarer medium water, then it bends away the normal.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
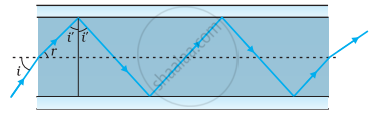
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of a material of refractive index 1·6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1·3, find its new focal length.
A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
A point ‘O’ marked on the surface of a glass sphere of diameter 20 cm is viewed through glass from the position directly opposite to the point O. If the refractive index of the glass is 1.5, find the position of the image formed. Also, draw the ray diagram for the formation of the image.
What is relative refractive index?
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
What is mirage?
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
