Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
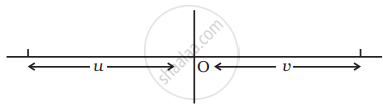
In many experimental set-ups the source and screen are fixed at a distance say D and the lens is movable. Show that there are two positions for the lens for which an image is formed on the screen. Find the distance between these points and the ratio of the image sizes for these two points.
उत्तर
From the reversibility of u and v, as seen from the formula for lens,
`1/f = 1/v - 1/u`
It is clear that there are two positions for which there shall be an image on the screen.
Let the first position be when the lens is at O.
Given `-u + v = D`
⇒ `u = -(D - v)`
Placing it in the lens formula
`1/(D - v) + 1/v = 1/f`
⇒ `(v + D - v)/((D - v)v) = 1/f`
⇒ `v^2 - Dv + Df` = 0
⇒ `v^2 = D/2 +- sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)/2`
`u = -(D - v) = - (D/2 + sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)/2)`
Thus, if the object distance is `D/2 - sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)/2` then the image is at `D/2 + sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)/2`
If the object distance is `D/2 + sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)/2`, then the image is at `D/2 - sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)/2`.
The distance between the poles for these two object distances is
`D/2 - sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)/2 - (D/2 - sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)/2) = sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)`
Let `d = sqrt(D^2 - 4Df)`
If `u = D/2 + d/2` then the image is at `v = D/2 - d/2`
∴ The magnification `m_1 = (D - d)/(D + d)`
If `u = (D - d)/2` then `v = (D + d)/2`
∴ The magnification `m_2 = (D + d)/(D - d)` Thus `m_2/m_1 = ((D + d)/(D - d))^2`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
You have learnt that plane and convex mirrors produce virtual images of objects. Can they produce real images under some circumstances? Explain.
The image of a small electric bulb fixed on the wall of a room is to be obtained on the opposite wall 3 m away by means of a large convex lens. What is the maximum possible focal length of the lens required for the purpose?
A screen is placed 90 cm from an object. The image of the object on the screen is formed by a convex lens at two different locations separated by 20 cm. Determine the focal length of the lens.
- Determine the ‘effective focal length’ of the combination of the two lenses, if they are placed 8.0 cm apart with their principal axes coincident. Does the answer depend on which side of the combination a beam of parallel light is incident? Is the notion of the effective focal length of this system useful at all?
- An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40 cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system and the size of the image.
An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40 cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system, and the size of the image
A card sheet divided into squares each of size 1 mm2 is being viewed at a distance of 9 cm through a magnifying glass (a converging lens of focal length 9 cm) held close to the eye.
- What is the magnification produced by the lens? How much is the area of each square in the virtual image?
- What is the angular magnification (magnifying power) of the lens?
- Is the magnification in (a) equal to the magnifying power in (b)? Explain.
An equiconvex lens of focal length 'f' is cut into two identical plane convex lenses. How will the power of each part be related to the focal length of the original lens ?
Two concave lenses L1 and L2 are kept in contact with each other. If the space between the two lenses is filled with a material of smaller refractive index, the magnitude of the focal length of the combination
An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s and stops at the focus. The image ______.
In the given figure the radius of curvature of the curved face in the planoconvex and the planoconcave lens is 15 cm each. The refractive index of the material of the lenses is 1.5. Find the final position of the image formed.