Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose you are inside the water in a swimming pool near an edge. A friends is standing on the edge. Do you find your friend taller or shorter than his usual height?
उत्तर
When viewed from the water, the friend will seem taller than his usual height.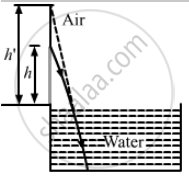
Let actual height be h and the apparent height be h'.
Here, the refraction is taking place from rarer to denser medium and a virtual image is formed.
Using
\[\frac{\mu_1}{- u} + \frac{\mu_2}{v} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{R}\]
Where refractive index of water is μ2 and refractive index of air is μ1.
u and v are object and image distances, respectively.
R is the radius of curvature, here we will take it as ∞.
\[\frac{\mu_1}{- u} + \frac{\mu_2}{v} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{\infty}\]
\[\frac{\mu_1}{u} = \frac{\mu_2}{v}\]
\[v = \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} \times u\]
We know magnification is given by:
\[m = \frac{v}{u}\]
Putting the value of v in the above equation:
\[m = \frac{u \times \mu_2}{u}\]
\[m = \mu_2 \]
As the magnification is greater than 1, so the apparent height seems to be greater than actual height.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why can’t we see clearly through fog?
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
In the meterbridge experimental set up, shown in the figure, the null point ‘D’ is obtained at a distance of 40 cm from end A of the meterbridge wire. If a resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with R1, null point is obtained at AD = 60 cm. Calculate the values of R1 and R2.
What is linearly polarized light?
The image formed by a concave mirror
A parallel beam of light is incident on a converging lens parallel to its principal axis. As one moves away from the lens on the other side on its principal axis, the intensity of light
A point object O is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length f = 20 cm at a distance of 40 cm to the left of it. The diameter of the lens is 10 cm. An eye is placed 60 cm to right of the lens and a distance h below the principal axis. The maximum value of h to see the image is
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A concave mirror forms an image of 20 cm high object on a screen placed 5.0 m away from the mirror. The height of the image is 50 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.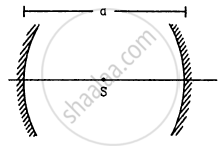
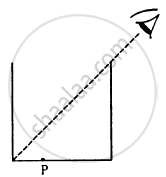
A cylindrical vessel, whose diameter and height both are equal to 30 cm, is placed on a horizontal surface and a small particle P is placed in it at a distance of 5.0 cm from the centre. An eye is placed at a position such that the edge of the bottom is just visible (see figure). The particle P is in the plane of drawing. Up to what minimum height should water be poured in the vessel to make the particle P visible?
Light falls from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Find the angle of incidence for which the angle of deviation is 90°.
A point source is placed at a depth h below the surface of water (refractive index = μ). (a) Show that light escapes through a circular area on the water surface with its centre directly above the point source. (b) Find the angle subtended by a radius of the area on the source.
A paperweight in the form of a hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm is used to hold down a printed page. An observer looks at the page vertically through the paperweight. At what height above the page will the printed letters near the centre appear to the observer?
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a secondary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Answer the following question in detail.
Is it possible to see primary and secondary rainbow simultaneously? Under what conditions?
Pick the wrong answer in the context with rainbow.
A plano-convex lens is made of material having refractive index 1.5. The radius of curvature of curved surface is 40 cm. The focal length of the lens is ____________ cm.
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
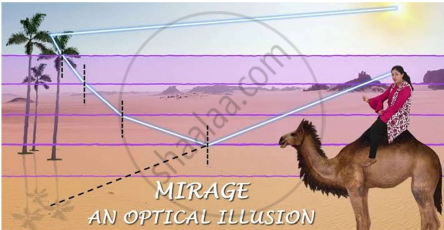 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
A diver at a depth 12 m inside water `(a_(µω) = 4/3)` sees the sky in a cone of semi-vertical angle
