Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A concave mirror forms an image of 20 cm high object on a screen placed 5.0 m away from the mirror. The height of the image is 50 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
उत्तर
Given,
Height of the object, h1 = 20 cm,
Distance of image from screen v = −5.0 m = −500 cm,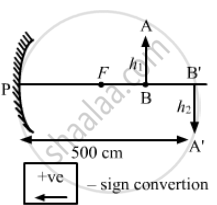
\[- \frac{v}{u} = \frac{h_2}{h_1}\]
\[or \frac{- ( - 500)}{u} = \frac{50}{20}\]
Where 'u' is the distance of object from screen.
(As the image is inverted)
Using mirror formula,
\[\frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[or \frac{1}{- 5} + \frac{1}{- 2} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[or - \frac{1}{f} = \frac{7}{10}\]
\[or f = - \frac{10}{7} = - 1 . 44 \text{ m }\]
Hence, the required focal length of the concave mirror is 1.44 m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Why can’t we see clearly through fog?
Draw the intensity distribution for the diffraction bands produced due to single slit ?
Write two points of difference between the phenomena of interference and diffraction.
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A point object O is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length f = 20 cm at a distance of 40 cm to the left of it. The diameter of the lens is 10 cm. An eye is placed 60 cm to right of the lens and a distance h below the principal axis. The maximum value of h to see the image is
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A 1 cm object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 7.5 cm. Find its distance from the mirror if the image formed is 0.6 cm in size.
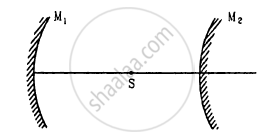
A converging mirror M1, a point source S and a diverging mirror M2 are arranged as shown in figure. The source is placed at a distance of 30 cm from M1. The focal length of each of the mirrors is 20 cm. Consider only the images formed by a maximum of two reflections. It is found that one image is formed on the source itself. (a) Find the distance between the two mirrors. (b) Find the location of the image formed by the single reflection from M2.
An optical fibre (μ = 1.72) is surrounded by a glass coating (μ = 1.50). Find the critical angle for total internal reflection at the fibre-glass interface.
A biconvex thick lens is constructed with glass (μ = 1.50). Each of the surfaces has a radius of 10 cm and the thickness at the middle is 5 cm. Locate the image of an object placed far away from the lens.
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a secondary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Answer the following question in detail.
Is it possible to see primary and secondary rainbow simultaneously? Under what conditions?
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
