Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
उत्तर
Given,
Radius (R) of the cylindrical rod = 1.0 cm
Refractive index (μg) of the rod = 1.5 = \[\frac{3}{2}\] Refractive index (μw) of water = 4/3 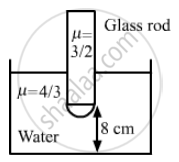
\[\frac{\mu_g}{v} - \frac{\mu_w}{u} = \frac{\mu_g - \mu_w}{R}\]
As per the question, u = −8 cm.
Now,
\[\frac{3}{2v} - \left( - \frac{4}{3 \times 8} \right) = \frac{\frac{3}{2} - \frac{4}{3}}{1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{3}{2v} + \frac{1}{6} = \frac{1}{6}\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = \infty\]
Hence, the image will be formed at infinity (∞).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
A point object O is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length f = 20 cm at a distance of 40 cm to the left of it. The diameter of the lens is 10 cm. An eye is placed 60 cm to right of the lens and a distance h below the principal axis. The maximum value of h to see the image is
A concave mirror forms an image of 20 cm high object on a screen placed 5.0 m away from the mirror. The height of the image is 50 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
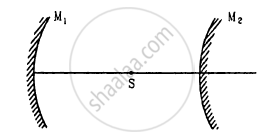
A converging mirror M1, a point source S and a diverging mirror M2 are arranged as shown in figure. The source is placed at a distance of 30 cm from M1. The focal length of each of the mirrors is 20 cm. Consider only the images formed by a maximum of two reflections. It is found that one image is formed on the source itself. (a) Find the distance between the two mirrors. (b) Find the location of the image formed by the single reflection from M2.
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

Light falls from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Find the angle of incidence for which the angle of deviation is 90°.
A paperweight in the form of a hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm is used to hold down a printed page. An observer looks at the page vertically through the paperweight. At what height above the page will the printed letters near the centre appear to the observer?
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a primary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Rainbow is the phenomenon due to ______.
State any one difference between a primary rainbow and a secondary rainbow.
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
A diamond is immersed in such a liquid which has its refractive index with respect to air as greater than the refractive index of water with respect to air. Then the critical angle of diamond-liquid interface as compared to critical angle of diamond-water interface will
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
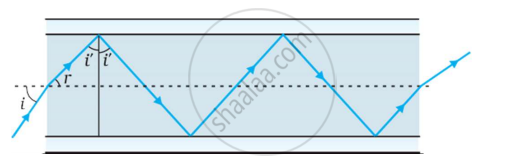
The following figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fiber of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for the following phenomena to occur.
The sky would appear red instead of blue if
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is ______.
Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because ______.
- light scattered into this region interfere destructively.
- there is no light scattered into this region.
- light is absorbed in this region.
- angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°.
