Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
Solution
Given,
Radius (R) of the cylindrical rod = 1.0 cm
Refractive index (μg) of the rod = 1.5 = 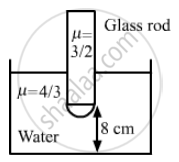
As per the question, u = −8 cm.
Now,
Hence, the image will be formed at infinity (∞).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Why can’t we see clearly through fog?
Name the phenomenon responsible for it.
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
What is linearly polarized light?
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
A candle flame 1.6 cm high is imaged in a ball bearing of diameter 0.4 cm. If the ball bearing is 20 cm away from the flame, find the location and the height of the image.
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.50) to water (μ = 1.33). Find the range of the angle of deviation for which there are two angles of incidence.
Light falls from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Find the angle of incidence for which the angle of deviation is 90°.
A container contains water up to a height of 20 cm and there is a point source at the centre of the bottom of the container. A rubber ring of radius r floats centrally on the water. The ceiling of the room is 2.0 m above the water surface. (a) Find the radius of the shadow of the ring formed on the ceiling if r = 15 cm. (b) Find the maximum value of r for which the shadow of the ring is formed on the ceiling. Refractive index of water = 4/3.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
Explain: ‘How is a rainbow formed’?
Answer the following question in detail.
State the conditions under which a rainbow can be seen.
Pick the wrong answer in the context with rainbow.
Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because ______.
- light scattered into this region interfere destructively.
- there is no light scattered into this region.
- light is absorbed in this region.
- angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°.
