Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
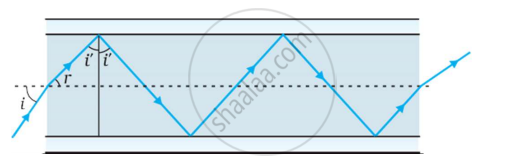
The following figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fiber of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for the following phenomena to occur.
पर्याय
0 < i < 90°
0 < i < 60°
0 < i < 45°
0 < i < 30°
उत्तर
0 < i < 60°
Explanation -
`1_(mu_2) = 1/(Sin "C'")`
Sin C' = `1.44/1.68` = 0.8571
C' ⇒ 59°
Total internal reflection will occur if the angle `"i'" > "i"_"c"^"'"`,
i.e., if i' > 59° or when r < rmax’ where rmax = 90° – 59° = 31°.
Using Snell’s law,
`("Sin" "i"_"max")/("Sin" "r"_"max")` = 1.68
or Sin imax = 1.68 × Sin rmax
= 1.68 × sin 31°
= 1.68 × 0.5150
= 0.8662
∴ imax = 60°
Thus all incident rays which make angles in the range 0 < i < 60° with the axis of the pipe will suffer total internal reflections in the pipe.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised light from Sun gets linearly polarised by scattering.
What is linearly polarized light?
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Find the position or positions of an object for which the image-size is double of the object-size.
A 1 cm object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 7.5 cm. Find its distance from the mirror if the image formed is 0.6 cm in size.
A 3 cm tall object is placed at a distance of 7.5 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 6 cm. Find the location, size and nature of the image.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.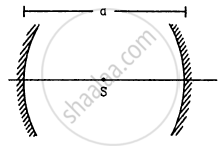
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a primary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
A diamond is immersed in such a liquid which has its refractive index with respect to air as greater than the refractive index of water with respect to air. Then the critical angle of diamond-liquid interface as compared to critical angle of diamond-water interface will
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
