Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.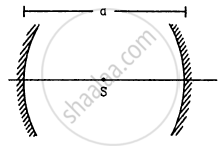
उत्तर
Given,
Two converging mirrors having equal focal length 'f '.
Both the mirrors will produce one image under two conditions:
Case-1
When the point source is at the centre of curvature of the mirrors, i.e, at a distance of '2f' from each mirror, the images will be produced at the same point 'S'. Therefore, d = 2f + 2f = 4f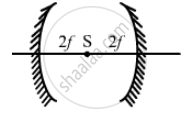
Case-II
When the point source 'S' is at focus, i.e., at a distance 'f ' from each mirror, the rays from the source after reflecting from one mirror will become parallel and so these parallel rays, after the reflection from the other mirror the object itself. Thus, only one image is formed.
Here d = f + f = 2f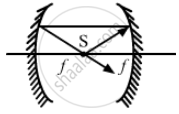
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
What is linearly polarized light?
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index
\[1 \cdot 2\] Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A 1 cm object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 7.5 cm. Find its distance from the mirror if the image formed is 0.6 cm in size.
A candle flame 1.6 cm high is imaged in a ball bearing of diameter 0.4 cm. If the ball bearing is 20 cm away from the flame, find the location and the height of the image.
A 3 cm tall object is placed at a distance of 7.5 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 6 cm. Find the location, size and nature of the image.
An optical fibre (μ = 1.72) is surrounded by a glass coating (μ = 1.50). Find the critical angle for total internal reflection at the fibre-glass interface.
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.50) to water (μ = 1.33). Find the range of the angle of deviation for which there are two angles of incidence.
Light falls from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Find the angle of incidence for which the angle of deviation is 90°.
A point source is placed at a depth h below the surface of water (refractive index = μ). (a) Show that light escapes through a circular area on the water surface with its centre directly above the point source. (b) Find the angle subtended by a radius of the area on the source.
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Answer the following question in detail.
Is it possible to see primary and secondary rainbow simultaneously? Under what conditions?
Rainbow is the phenomenon due to ______.
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
A diamond is immersed in such a liquid which has its refractive index with respect to air as greater than the refractive index of water with respect to air. Then the critical angle of diamond-liquid interface as compared to critical angle of diamond-water interface will
