Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
उत्तर
A polaroid consists of long-chain molecules aligned in a particular direction. The electric vectors (associated with the propagating light wave) along the direction of the aligned molecules get absorbed. Thus, if an unpolarized light wave is an incident on such a Polaroid, the light wave will get linearly polarised with the electric vector oscillating along a direction known as the pass-axis of the polaroid, perpendicular to the aligned molecules. Therefore, if the light from an ordinary source passes through a polaroid sheet, its intensity is reduced by half. Rotating the Polaroid has no effect on the transmitted beam, and the transmitted intensity remains constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the meterbridge experimental set up, shown in the figure, the null point ‘D’ is obtained at a distance of 40 cm from end A of the meterbridge wire. If a resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with R1, null point is obtained at AD = 60 cm. Calculate the values of R1 and R2.
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A 1 cm object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 7.5 cm. Find its distance from the mirror if the image formed is 0.6 cm in size.
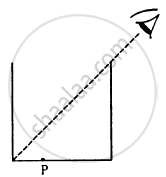
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

A cylindrical vessel, whose diameter and height both are equal to 30 cm, is placed on a horizontal surface and a small particle P is placed in it at a distance of 5.0 cm from the centre. An eye is placed at a position such that the edge of the bottom is just visible (see figure). The particle P is in the plane of drawing. Up to what minimum height should water be poured in the vessel to make the particle P visible?
A biconvex thick lens is constructed with glass (μ = 1.50). Each of the surfaces has a radius of 10 cm and the thickness at the middle is 5 cm. Locate the image of an object placed far away from the lens.
Answer the following question in detail.
State the conditions under which a rainbow can be seen.
Answer the following question in detail.
Is it possible to see primary and secondary rainbow simultaneously? Under what conditions?
A plano-convex lens is made of material having refractive index 1.5. The radius of curvature of curved surface is 40 cm. The focal length of the lens is ____________ cm.
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
