Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the meterbridge experimental set up, shown in the figure, the null point ‘D’ is obtained at a distance of 40 cm from end A of the meterbridge wire. If a resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with R1, null point is obtained at AD = 60 cm. Calculate the values of R1 and R2.
उत्तर
Considering both the situations and writing them in the form of equations
Let R' be the resistance per unit length of the potential meter wire,
`R_1/R_2 = (R' xx 40)/(R'(100 -40) ) = 40/60 = 2/3`
`(R_1 + 10)/R_2 = (R' xx 60)/(R'(100 -60)) = 60/40 = 3/2`
`R_1/R_2 = 2/3 -------- (1)`
`(R_1 +10)/R_2 = 3/2 ---------(2)`
Putting the value of R1 from equation (1) and substituting in equation (2)
`2/3 + 10/R_2 = 3/2`
`R_2 = 12Ω`
Reca;;omg equation (1) again
`R_1/12 = 2/3`
`R_1 = 8Ω`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
A 1 cm object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 7.5 cm. Find its distance from the mirror if the image formed is 0.6 cm in size.
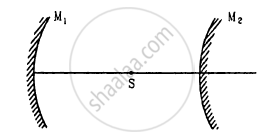
A converging mirror M1, a point source S and a diverging mirror M2 are arranged as shown in figure. The source is placed at a distance of 30 cm from M1. The focal length of each of the mirrors is 20 cm. Consider only the images formed by a maximum of two reflections. It is found that one image is formed on the source itself. (a) Find the distance between the two mirrors. (b) Find the location of the image formed by the single reflection from M2.
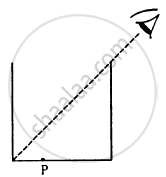
A cylindrical vessel, whose diameter and height both are equal to 30 cm, is placed on a horizontal surface and a small particle P is placed in it at a distance of 5.0 cm from the centre. An eye is placed at a position such that the edge of the bottom is just visible (see figure). The particle P is in the plane of drawing. Up to what minimum height should water be poured in the vessel to make the particle P visible?
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
State any one difference between a primary rainbow and a secondary rainbow.
Explain the formation of primary and secondary rainbow.
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because ______.
- light scattered into this region interfere destructively.
- there is no light scattered into this region.
- light is absorbed in this region.
- angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°.
