Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
उत्तर
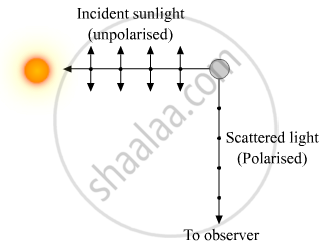
The incident sunlight is unpolarised. The dot and double arrows show the polarization in the perpendicular and in the plane of the figure. Under the influence of the electric field of the incident wave, the electrons in the molecules of the atmosphere acquire components of motion in both these directions. An observer looking at 90° to the direction of the sun, the charges accelerating parallel to the double arrows do not radiate energy towards this observer since their acceleration has no transverse component. The radiation scattered by the molecule is therefore represented by dots. It is linearly polarized perpendicular to the plane of the figure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Name the phenomenon responsible for it.
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
A concave mirror forms an image of 20 cm high object on a screen placed 5.0 m away from the mirror. The height of the image is 50 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
k transparent slabs are arranged one over another. The refractive indices of the slabs are μ1, μ2, μ3, ... μk and the thicknesses are t1 t2, t3, ... tk. An object is seen through this combination with nearly perpendicular light. Find the equivalent refractive index of the system which will allow the image to be formed at the same place.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a primary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
A plano-convex lens is made of material having refractive index 1.5. The radius of curvature of curved surface is 40 cm. The focal length of the lens is ____________ cm.
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
A diamond is immersed in such a liquid which has its refractive index with respect to air as greater than the refractive index of water with respect to air. Then the critical angle of diamond-liquid interface as compared to critical angle of diamond-water interface will
