Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
उत्तर
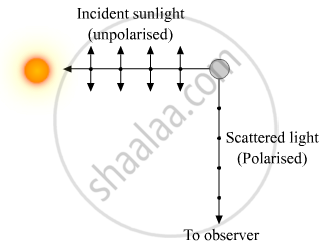
The incident sunlight is unpolarised. The dot and double arrows show the polarization in the perpendicular and in the plane of the figure. Under the influence of the electric field of the incident wave, the electrons in the molecules of the atmosphere acquire components of motion in both these directions. An observer looking at 90° to the direction of the sun, the charges accelerating parallel to the double arrows do not radiate energy towards this observer since their acceleration has no transverse component. The radiation scattered by the molecule is therefore represented by dots. It is linearly polarized perpendicular to the plane of the figure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
What is linearly polarized light?
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index
\[1 \cdot 2\] Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.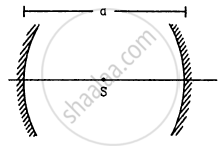
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a secondary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
State any one difference between a primary rainbow and a secondary rainbow.
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is ______.
