Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
k transparent slabs are arranged one over another. The refractive indices of the slabs are μ1, μ2, μ3, ... μk and the thicknesses are t1 t2, t3, ... tk. An object is seen through this combination with nearly perpendicular light. Find the equivalent refractive index of the system which will allow the image to be formed at the same place.
उत्तर
k number of transparent slabs are arranged one over the other.
Refractive indices of the slabs = μ1, μ2, μ3, ..., μk
Thickness of the slabs = t1, t2, t3,.., tk
Shift due to one slab: \[∆ t = \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu} \right]t\]
For the combination of multiple slabs, the shift is given by,
\[∆ t = \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_1} \right] t_1 + \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_2} \right] t_2 + . . . + \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_k} \right] t_k . . . (i)\]|
Let μ be the refractive index of the combination of slabs.
The image is formed at the same place.
So, the shift will be:
\[\Delta t = \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{\mu} \right) \right]( t_1 + t_2 . . . + t_k ) . . . (ii)\]
Equating (i) and (ii), we get:
\[\left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{\mu} \right) \right]( t_1 + t_2 . . . + t_k ) = \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_1} \right] t_1 + \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_2} \right] t_2 + \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_k} \right] t_k \]
\[ = ( t_1 + t_2 . . . + t_k ) - \left( \frac{t_1}{\mu_1} + \frac{t_2}{\mu_2} + \frac{t_k}{\mu_k} \right)\]
\[ = - \frac{1}{\mu} \sum^k_{i = 1} t_i = - \sum^k_{i = 1} \left( \frac{t_i}{\mu_i} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu = \frac{\sum^k_{i = 1} t_i}{- \sum^k_{i = 1} \left( \frac{t_i}{\mu_i} \right)}\]
Hence, the required equivalent refractive index is
\[\frac{\sum^k_{i = 1} t_i}{\sum^k_{i = 1} \left( \frac{t_i}{\mu_i} \right)}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw the intensity distribution for the diffraction bands produced due to single slit ?
Write two points of difference between the phenomena of interference and diffraction.
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
What is linearly polarized light?
Suppose you are inside the water in a swimming pool near an edge. A friends is standing on the edge. Do you find your friend taller or shorter than his usual height?
A 1 cm object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 7.5 cm. Find its distance from the mirror if the image formed is 0.6 cm in size.
A candle flame 1.6 cm high is imaged in a ball bearing of diameter 0.4 cm. If the ball bearing is 20 cm away from the flame, find the location and the height of the image.
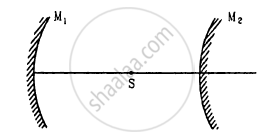
A converging mirror M1, a point source S and a diverging mirror M2 are arranged as shown in figure. The source is placed at a distance of 30 cm from M1. The focal length of each of the mirrors is 20 cm. Consider only the images formed by a maximum of two reflections. It is found that one image is formed on the source itself. (a) Find the distance between the two mirrors. (b) Find the location of the image formed by the single reflection from M2.
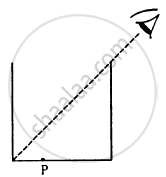
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

A cylindrical vessel, whose diameter and height both are equal to 30 cm, is placed on a horizontal surface and a small particle P is placed in it at a distance of 5.0 cm from the centre. An eye is placed at a position such that the edge of the bottom is just visible (see figure). The particle P is in the plane of drawing. Up to what minimum height should water be poured in the vessel to make the particle P visible?
Light falls from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Find the angle of incidence for which the angle of deviation is 90°.
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
A plano-convex lens is made of material having refractive index 1.5. The radius of curvature of curved surface is 40 cm. The focal length of the lens is ____________ cm.
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 5890 Å falls normally on a slit of width 0.2 mm. Find the distance between the first minima on the two sides of the central maximum of the diffraction pattern observed on a screen placed in the focal plane of a convex lens of focal length 50 cm. The lens is placed quite close to the slit.
The sky would appear red instead of blue if
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is ______.
