Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 20 cm, the image formed will be ______.
विकल्प
Real and 20 cm in front of the mirror
Real and 6.67 cm in front of the mirror.
Virtual and 20 cm behind the mirror.
Virtual and 6.67 cm behind the mirror.
उत्तर
If an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 20 cm, the image formed will be virtual and 20 cm behind the mirror.
Explanation:
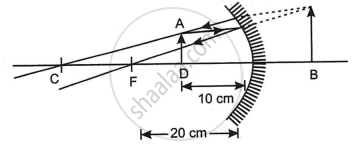
Given, f = - 20 cm; u = - 10 cm
Using the formula
`1/"f" = 1/"v" + 1/"u"`
`=> 1/(- 20) = 1/v - 1/10`
`=> 1/10 - 1/20 = 1/v`
`=> 1/v = 1/20`
⇒ v = 20 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
In image formation from spherical mirrors, only paraxial rays are considered because they
A converging lens of focal length 12 cm and a diverging mirror of focal length 7.5 cm are placed 5.0 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed so that its image falls on itself?
A converging lens and a diverging mirror are placed at a separation of 15 cm. The focal length of the lens is 25 cm and that of the mirror is 40 cm. Where should a point source be placed between the lens and the mirror so that the light, after getting reflected by the mirror and then getting transmitted by the lens, comes out parallel to the principal axis?
Answer the following question.
Three lenses of focal length +10 cm, —10 cm and +30 cm are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.

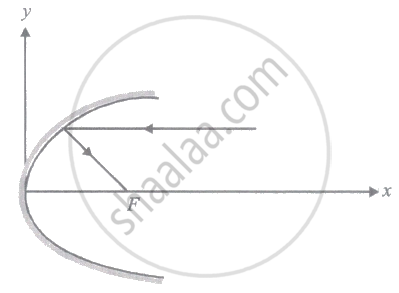
A parallel beam of light ray parallel to the x-axis is incident on a parabolic reflecting surface x = 2by2 as shown in the figure. After reflecting it passes through focal point F. What is the focal length of the reflecting surface?
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h–1 on a straight road. Looking at the rear view mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h–1. In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 s till the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
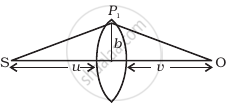
(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Figure). Let the thickness of the lens vary as `w(b) = w_0 - b^2/α`, where b is the verticle distance from the pole. `w_0` is a constant. Using Fermat’s principle i.e. the time of transit for a ray between the source and observer is an extremum, find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.
(ii) A gravitational lens may be assumed to have a varying width of the form
`w(b) = k_1ln(k_2/b) b_("min") < b < b_("max")`
= `k_1ln (K_2/b_("min")) b < b_("min")`
Show that an observer will see an image of a point object as a ring about the center of the lens with an angular radius
`β = sqrt((n - 1)k_1 u/v)/(u + v)`
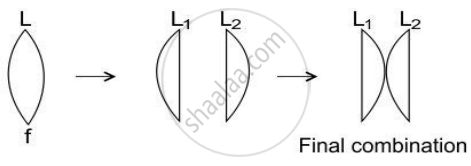
A lens of focal length f is divided into two equal parts and then these parts are put in a combination as shown in the figure below.
- What is the focal length of L1?
- What is the focal length of the final combination?