Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The adjacent diagram shows two right-angled isosceles prisms A and B. Complete the diagram to show the path of rays P and Q emerging out of the prism B. What principles have you used to complete the diagram?
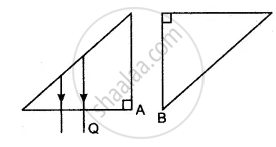
Solution
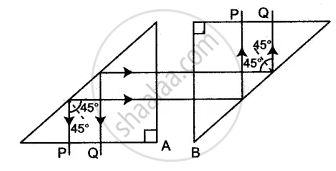
The completed ray diagram is shown in the figure.
Following two principles are used to complete the diagram:
(1) A ray of light incident normally on the interface of two media passes undeviated.
(2) A ray of light striking the interface of two media (glass and air) from glass, at an angle of incidence, equal to 45° (which is greater than the critical angle = 42°) suffers total internal reflection.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following phenomena/ applications: P) Mirage, Q) rainbow, R) Optical fibre and S) glittering of a diamond. Total internal reflection is involved in
Choose the correct option.
Select the WRONG statement.
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
Solve Numerical example.
From the given data set, determine angular dispersion by the prism and dispersive power of its material for extreme colours. nR = 1.62 nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
Observe the given figure and write appropriate phenomenon of light in the box.

The resultant `vec"R"` of `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is perpendicular to `vec"P"`. Also `|vec"P"|=|vec"R"|`. The angle between `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is ______.
[tan 45° = 1]
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index µ, the angle of incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. Then the angle of incidence is ______.
The diagram below shows a fish in the tank and its image seen in the surface of water.

Name the phenomenon responsible for the formation of this image.
