Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
Solution
- Absolute refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in the given medium.
- A stick or pencil kept obliquely in a glass containing water appears broken as its part in water appears to be raised.
- As the speed of light is different in two media, the rays of light coming from water undergo refraction at the boundary separating the two media.
- Consider the speed of light to be v in water and c in air. (Speed of light in air ≈ speed of light in vacuum)
∴ refractive index of water = `"n"_"w"/"n"_"a"="n"_"w"/"n"_"vacuum"="c"/"v"` - The relative refractive index of a medium 2 is the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 and it is defined as the ratio of the speed of light v1 in medium 1 to its speed v2 in medium 2.
∴ The relative refractive index of medium 2,
1n2 = `"v"_1/"v"_2` - Consider a beaker filled with water of absolute refractive index n1 kept on a transparent glass slab of absolute refractive index n2.
- Thus, the refractive index of water with respect to that of glass will be,
gnw = `"n"_2/"n"_1=("c"/"v"_2)/("c"/"v"_1)="v"_1/"v"_2`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
A diver under water, looks obliquely at a fisherman standing on the bank of a lake. Would the fisherman look taller or shorter to the diver than what he actually is?
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of a material of refractive index 1·6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1·3, find its new focal length.
Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) diffraction
(d) dispersion.
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.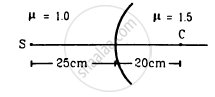
A converging beam of light traveling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1⋅5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of, the image. Also, draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
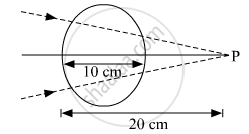
Choose the correct option.
There are different fish, monkeys, and water of the habitable planet of the star Proxima b. A fish swimming underwater feels that there is a monkey at 2.5 m on the top of a tree. The same monkey feels that the fish is 1.6 m below the water surface. Interestingly, height of the tree and the depth at which the fish is swimming are exactly same. Refractive index of that water must be
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Why do stars twinkle?
What is Snell’s window?
How does an endoscope work?
A ray of light passes through equilateral prism such that the angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence and each of these angles is equal to `(3/4)^"th"` the angle of prism. The angle of deviation is ______.
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices µ1 > µ2 > µ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is `h/3`. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
