Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Solution
Light from object O at the bottom passes from denser (water) to rarer medium (air).
n1 and n2 are refractive of denser and rarer medium.
By snells law
n1 sin i = n2 sin r
sin i ≈ tan i, as i and r are small
n1 tan i ≈ n2 tan i
`"n"_1 "DB"/"DO" = "n"_2 "DB"/"DI"`
`"n"_1/"d" = "n"_2/"d'"`
`"d'"/"d" = "n"_2/"n"_1`
`"d'" = "n"_2/"n"_1 xx "d"`
If n2 = 1 and n1 = n
d' = `"d"/"n"`
d' - d = d`(1 - 1/"n")`
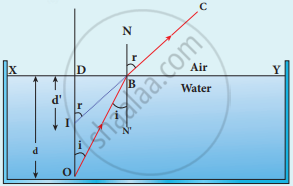
Apparent depth
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
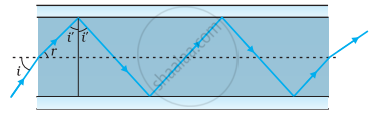
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is 1.33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
A laser light is focussed by a converging lens. Will there be a significant chromatic aberration?
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
Why do stars twinkle?
What is mirage?
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
