Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Current Electricity
3: Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
4: Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
5: Electromagnetic waves
▶ 6: Ray Optics
7: Wave Optics
8: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
9: Atomic and Nuclear physics
10: Electronics and Communication
11: Recent Developments in Physics
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Ray Optics Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Ray Optics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Ray Optics
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board 6 Ray Optics Evaluation [Pages 48 - 51]
Multiple choice questions
The speed of light in an isotropic medium depends on, ______.
its intensity
its wavelength
the nature of propagation
the motion of the source w.r.t medium
A rod of length 10 cm lies along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm in such a way that its end closer to the pole is 20 cm away from the mirror. The length of the image is,
2.5 cm
5 cm
10 cm
15 cm
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror of focal length of f and the maximum and minimum distance of an object from the mirror such that the image formed is real and magnified.
2f and c
c and ∞
f and O
None of these
For light incident from air on a slab of refractive index 2, the maximum possible angle of refraction is ______.
30°
45°
60°
90°
If the velocity and wavelength of light in air is Va and λa and that in water is Va and λw, then the refractive index of water is ______.
`"V"_"w"/"V"_"a"`
`"V"_"a"/"V"_"w"`
`lambda_"w"/lambda_"a"`
`("V"_"a"lambda)/("V"_"w"lambdaw_"")`
Stars twinkle due to ______.
reflection
total internal reflection
refraction
polarisation
When a biconvex lens of glass having refractive index 1.47 is dipped in a liquid, it acts as a plane sheet of glass. This implies that the liquid must have refractive index.
less than one
less than that of glass
greater than that of glass
equal to that of glass
The radius of curvature of curved surface at a thin planoconvex lens is 10 cm and the refractive index is 1.5. If the plane surface is silvered, then the focal length will be.
5 cm
10 cm
15 cm
20 cm
An air bubble in glass slab of refractive index 1.5 (near normal incidence) is 5 cm deep when viewed from one surface and 3 cm deep when viewed from the opposite face. The thickness of the slab is,
8 cm
10 cm
12 cm
16 cm
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index n falls, on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidents of 45°. The ray can undergo total internal reflection for the following n.
n = 1.25
n = 1.33
n = 1.4
n = 1.5
Short Answer Questions
What is angle of deviation due to reflection?
Derive the relation between f and R for a spherical mirror.
What are the Cartesian sign conventions for a spherical mirror?
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
State the laws of refraction.
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
What is a principle of reversibility?
What is relative refractive index?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Why do stars twinkle?
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
What is mirage?
What is looming?
Write a short note on the prisms making use of total internal reflection.
What is Snell’s window?
How does an endoscope work?
What are primary focus and secondary focus of convex lens?
What are the sign conventions followed for lenses?
Write a note on optical fibre.
Arrive at lens equation from lens maker’s formula.
Obtain the equation for lateral magnification for thin lens.
What is power of a lens?
Derive the equation for effective focal length for lenses in contact.
What is angle of minimum deviation?
What is dispersion?
How are rainbows formed?
What is Rayleigh’s scattering?
Why does sky appear blue?
What is the reason for reddish appearance of sky during sunset and sunrise?
Why do clouds appear white?
Long Answer Questions
Derive the mirror equation and the equation for lateral magnification.
Describe Fizeau’s method to determine the speed of light.
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
Derive the equation for acceptance angle and numerical aperture, of optical fiber.
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
Derive the equation for refraction at a single spherical surface.
Obtain lens maker’s formula and mention its significance.
Derive the equation for thin lens and obtain its magnification.
Derive the equation for an angle of deviation produced by a prism and thus obtain the equation for the refractive index of the material of the prism.
What is dispersion?
Obtain the equation for dispersive power of a medium
Conceptual Questions
Why are dish antennas curved?
What type of lens is formed by a bubble inside water?
It is possible for two lenses to produce zero power?
A biconvex lens has focal length f and intensity of light I passing through it. What will be the focal length and intensity for portions of lenses obtained by cutting it vertically and horizontally as shown in the figure?

Why is yellow light preferred to during fog?
Numerical Problems
An object of 4 cm height is placed at 6 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 24 cm. Find the position, height, magnification and nature of the image.
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. The image formed is three times the size of the object. Calculate two possible distances of the object from the mirror.
A beam of light consisting of red, green and blue is incident on a right-angled prism as shown in figure. The refractive index of the material of the prism for the above red, green and blue colours are 1.39, 1.44 and 1.47 respectively. What are the colours suffer total internal reflection?
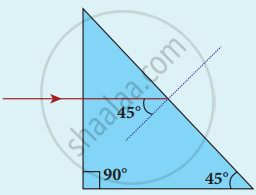
An object is placed at a certain distance from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the distance of the object if the image obtained is magnified 4 times.
Obtain the lens maker’s formula for a lens of refractive index n2 which is separating two media of refractive indices n1 and n3 on the left and right respectively.
A thin converging glass lens made of glass with refractive index 1.5 has a power of + 5.0 D. When this lens is immersed in a liquid of refractive index n, it acts as a divergent lens of focal length 100 cm. What must be the value of n?
If the distance D between an object and screen is greater than 4 times the focal length of a convex lens, then there are two positions of the lens for which images are formed on the screen. This method is called conjugate foci method. If d is the distance between the two positions of the lens, obtain the equation for a focal length of the convex lens.
Prove that a convex lens can only form a virtual, erect and diminished image.
A point object is placed at 20 cm from a thin plano-convex lens of focal length 15 cm whose plane surface is silvered. Locate the position and nature of the final image.
Find the ratio of the intensities of lights with wavelengths 500 nm and 300 nm which undergo Rayleigh scattering.
Solutions for 6: Ray Optics
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Ray Optics Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Ray Optics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Ray Optics
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 6 (Ray Optics) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 Ray Optics are Speed of Light, Refraction, Refraction at Single Spherical Surface, Thin Lens, Prism, Theories on Light, Wave Nature of Light, Interference, Diffraction of Light, Optical Instruments, Polarisation, Introduction to Light, Spherical Mirrors.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board solutions Ray Optics exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Ray Optics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
