Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Current Electricity
3: Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
4: Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
5: Electromagnetic waves
6: Ray Optics
▶ 7: Wave Optics
8: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
9: Atomic and Nuclear physics
10: Electronics and Communication
11: Recent Developments in Physics
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 7 - Wave Optics Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 7 - Wave Optics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Wave Optics
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board 7 Wave Optics Evaluation [Pages 102 - 105]
Multiple choice questions
A plane glass is placed over a various coloured letters (violet, green, yellow, red) The letter which appears to be raised more is ______.
red
yellow
green
violet
Two point white dots are 1 mm apart on a black paper. They are viewed by eye of pupil diameter 3 mm approximately. The maximum distance at which these dots can be resolved by the eye is, [take wavelength of light, λ = 500 nm]
1 m
5 m
3 m
6 m
In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the slit separation is doubled. To maintain the same fringe spacing on the screen, the screen-to-slit distance D must be changed to ______.
2D
`"D"/2`
`sqrt2"D"`
`"D"/sqrt2`
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities I and 4I are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are ______.
5I and I
5I and 3I
9I and I
9I and 3I
When light is incident on a soap film of thickness 5 x 10-5 cm, the wavelength of light reflected maximum in the visible region is 5320 A. Refractive index of the film will be ______.
1.22
1.33
1.51
1.83
First diffraction minimum due to a single slit of width 1.0 × 10-5 cm is at 30°. Then wavelength of light used is ______.
400 Å
500 Å
600 Å
700 Å
A ray of light strikes a glass plate at an angle 60°. If the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other, the refractive index of the glass is ______.
`sqrt3`
`3/2`
`sqrt(3/2)`
2
One of Young’s double slits is covered with a glass plate as shown in figure. The position of central maximum will,
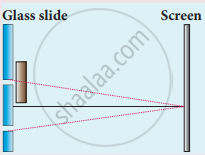
get shifted downwards
get shifted upwards
will remain the same
data insufficient to conclude
Light transmitted by Nicol prism is ______.
partially polarised
unpolarised
plane polarised
elliptically polarised
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
interference
diffraction
scattering
polarisation
Short Answer Questions
What are the salient features of corpuscular theory of light?
What are the important points of wave theory of light?
What is the significance of electromagnetic wave theory of light?
Write a short note on quantum theory of light.
Define a wavefront.
What are the shapes of wavefront for source at infinite?
What is the shape of wavefront for point source?
What is the shape of wavefront for line source?
State Huygen's principle.
What is interference of light?
What is phase of a wave?
Obtain the relation between phase difference and path difference.
Answer in brief:
What is meant by coherent sources?
How does wavefront division provide coherent sources?
What is intensity (or) amplitude division?
How do source and images behave as coherent sources?
What is a bandwidth of interference pattern?
What is diffraction?
Differentiate between Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction.
Discuss the special cases on first minimum in Fraunhofer diffraction.
What is Fresnel’s distance? Obtain the equation for Fresnel’s distance.
Mention the differences between interference and diffraction.
What is a diffraction grating?
What is resolution?
What is Rayleigh’s criterion?
What is the difference between resolution and magnification?
What is polarisation?
What is the difference between polarised light and unpolarised light?
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is a polariser?
What is a analyser?
What is plane polarised light?
What is unpolarised light?
What is partially polarised light?
State and obtain Malus’ law.
List the uses of polaroids.
State Brewster’s law.
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
Discuss about pile of plates.
What is double refraction?
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
Discuss about Nicol prism.
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
What is normal focusing?
What is the near point focusing?
Why is oil-immersed objective preferred in a microscope?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a reflecting telescope?
What is the use of an erecting lens in a terrestrial telescope?
What is the use of collimator in a spectrmeter?
What are the uses of spectrometer?
What is myopia?
What is the remedy of myopia?
What is hypermetropia?
What is the remedy of hypermetropia?
What is astigmatism? What is its remedy?
What is presbyopia?
Long Answer Questions
Prove laws of reflection using Huygens’ principle.
Prove laws of refraction using Huygens’ principle.
Obtain the equation for resultant intensity due to interference of light.
Explain Young’s double-slit experimental setup and obtain the equation for path difference.
Obtain the equation for bandwidth in Young’s double slit experiment.
Discuss the interference in thin films and obtain the equations for constructive and destructive interference for transmitted and reflected light.
Discuss diffraction at single slit and obtain the condition for nth minimum.
Discuss the diffraction at a grating and obtain the condition for the mth maximum.
Discuss the experiment to determine the wavelength of monochromatic light using a diffraction grating.
Discuss the experiment to determine the wavelength of different colours using diffraction grating.
Obtain the equation for resolving power of optical instrument
Discuss about simple microscope and obtain the equations for magnification for near point focusing and normal focusing.
Explain about the compound microscope and obtain the equation for magnification.
Obtain the equation for resolving the power of the microscope.
Discuss about astronomical telescope.
Mention different parts of the spectrometer.
Explain the preliminary adjustments of the spectrometer.
Explain the experimental determination of the material of the prism using a spectrometer.
Conceptual Questions
The ratio of maximum and minimum intensities in an interference pattern is 36 : 1. What is the ratio of the amplitudes of the two interfering waves?
In Young’s double-slit experiment, 62 fringes are seen in the visible region for sodium light of wavelength 5893 Å. If violet light of wavelength 4359 Å is used in place of sodium light, then what is the number of fringes seen?
Light of wavelength 600 nm that falls on a pair of slits producing interference pattern on a screen in which the bright fringes are separated by 7.2 mm. What must be the wavelength of another light which produces bright fringes separated by 8.1 mm with the same apparatus?
A beam of light of wavelength 600 nm from a distant source falls on a single slit 1 mm wide and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 2 m away. What is the distance between the first dark fringe on either side of the central bright fringe?
Light of wavelength of 5000 Å produces diffraction pattern of the single slit of width 2.5 μm. What is the maximum order of diffraction possible?
I0 is the intensity of light existing between two cross Polaroids kept with their axes perpendicular to each other. A third polaroid is introduced between them. What must be the angle between the axes of the first and the newly introduced polaroid to get the maximum light from the whole arrangement?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
The reflected light is found to be plane polarised when an unpolarized light falls on a denser medium at 60° with the normal. Find the angle of refraction and critical angle of incidence for total internal reflection in the denser to rarer medium reflection.
The near point and the far point for a person are 50 cm and 500 cm, respectively. Calculate the power of the lens the person should wear to read a book held in hand at 25 cm. What maximum distance is clearly visible for the person with this lens on the eye?
A compound microscope has a magnifying power of 100 when the image is formed at infinity. The objective has a focal length of 0.5 cm and the tube length is 6.5 cm. What is the focal length of the eyepiece.
Solutions for 7: Wave Optics
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 7 - Wave Optics Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 7 - Wave Optics - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 7 - Wave Optics
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 7 (Wave Optics) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 7 Wave Optics are Proof of Laws of Reflection and Refraction Using Huygens' Principle, Huygens' Principle, Theories on Light, Interference, Wave Nature of Light, Optical Instruments: Simple Microscope, Optical Instruments: Compound Microscope, Diffraction of Light, Polarisation, Optical Instruments, Optical Instruments: Telescope, Optical Instruments: Spectrometer, Optical Instruments: the Eye.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board solutions Wave Optics exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Wave Optics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
