Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss about simple microscope and obtain the equations for magnification for near point focusing and normal focusing.
Solution
- A simple microscope is a single magnifying (converging) lens of small focal length The idea is to get an erect, magnified and virtual image of the object.
- Near point focusing –
The image is formed at near point, i.e. 25 cm for normal eye. This distance is also called as least distance D of distinct vision. In this position, the eye feels comfortable but there is little strain on the eye. - Normal focusing –
The image is formed at infinity. In this position the eye is most relaxed to view the image.
> Object distance u is less than f. The image distance is the near point D. The magnification m is given by the relation,
m = `"v"/"u"` - With the help of lens equation,
`1/"v" − 1/"u" = 1/"f"` the magnification can further be written as,
m = 1 – `"v"/"f"` - Substituting for v with sign convention,
v = -D - m = `1 + "D"/"f"`
This is the magnification for near-point focusing.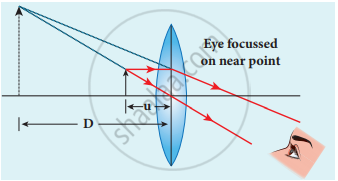
Near point focusing - The angular magnification is defined as the ratio of angle θi subtended by the image with an aided eye to the angle θ0 subtended by the object with the unaided eye.
m = `theta_"i"/theta_0`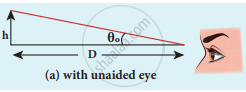
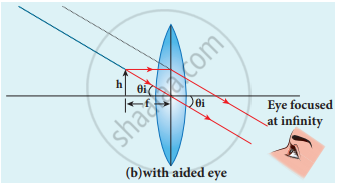
Normal focusing - For unaided eye shown in Figure (a),
tan θ0 ≈ θ0 = `"h"/"D"` - For aided eye shown in Figure (b),
tan θi ≈ θi = `"h"/"f"` - The angular magnification is,
m = `θ_"i"/θ_0` = `("h"//"f")/("h"//"D")`
m = `"D"/"f"`
This is the magnification for normal focusing.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question in detail.
Define and describe the magnifying power of an optical instrument.
Answer the following question in detail.
How does magnifying power differ from linear or lateral magnification?
Answer the following question in detail.
What is a terrestrial telescope and an astronomical telescope?
Answer the following question in detail.
What is the limitation in increasing the magnifying powers of a compound microscope?
What is the near point focusing?
Why is oil-immersed objective preferred in a microscope?
What is the use of collimator in a spectrmeter?
What is the remedy of myopia?
What is the remedy of hypermetropia?
What is presbyopia?
What is astigmatism? What is its remedy?
A compound microscope has a magnification of 30. The focal length of eye piece is 5 cm. Assuming the final image to be at least distance of distinct vision, find the magnification produced by the objective.
A compound microscope has a magnifying power of 100 when the image is formed at infinity. The objective has a focal length of 0.5 cm and the tube length is 6.5 cm. What is the focal length of the eyepiece.
The magnifying power of a telescope is nine. When it is adjusted for parallel rays, the distance between the objective and eyepiece is 20 cm. The focal length of objective and eyepiece are respectively.
An object viewed from a near point distance of 25 cm, using a microscopic lens with magnification '6', gives an unresolved image. A resolved image is observed at infinite distance with a total magnification double the earlier using an eyepiece along with the given lens and a tube of length 0.6 m, if the focal length of the eyepiece is equal to ______ cm.
Magnification produced by astronomical telescope for normal adjustment is 10 and length of telescope is 1.1 m. The magnification when the image is formed at least distance of distinct vision (D = 25 cm) is ______.
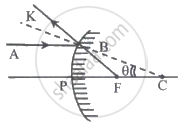
In the adjoining figure, AB represents the incident ray, and BK is the reflected ray. If angle BCF = θ, then ∠BFP is given by ______.
A camera objective has an aperture diameter of d. If the aperture is reduced to diameter d/2, the exposure time under identical conditions of light should be made ______.
