Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Current Electricity
▶ 3: Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
4: Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
5: Electromagnetic waves
6: Ray Optics
7: Wave Optics
8: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
9: Atomic and Nuclear physics
10: Electronics and Communication
11: Recent Developments in Physics
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 3 - Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 3 - Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board 3 Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current Evaluation [Pages 189 - 193]
Multiple choice questions
The magnetic field at the centre O of the following current loop is
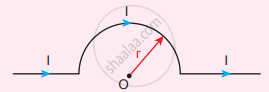
`(mu_circ "I")/(4"r")⊗`
`(mu_circ "I")/(4"r")⊙`
`(mu_circ "I")/(2"r")⊗`
`(mu_circ "I")/(2"r")⊙`
An electron moves straight inside a charged parallel plate capacitor of uniform charge density σ The time taken by the electron to cross the parallel plate capacitor when the plates of the capacitor are kept under constant magnetic field of induction `vec"B"` is-
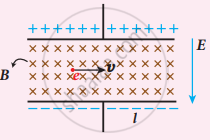
`epsilon_circ "elB"/sigma`
`epsilon_circ "lB"/(sigmal)`
`epsilon_circ "lB"/("e"sigma)`
`epsilon_circ "lB"/sigma`
A particle having mass m and charge q accelerated through a potential difference V. Find the force experienced when it is kept under perpendicular magnetic field B is
`sqrt((2"q"^3"BV")/"m")`
`sqrt(("q"^3"B"^2"V")/"2m")`
`sqrt(("2q"^3"B"^2"V")/"m")`
`sqrt(("2q"^3"B""V")/"m"^3)`
A circular coil of radius 5 cm and 50 turns carries a current of 3 ampere. The magnetic dipole moment of the coil is nearly
1.0 Am2
1.2 Am2
0.5 Am2
0.8 Am2
A thin insulated wire forms a plane spiral of N = 100 tight turns carrying a current 1 = 8 m A (milli ampere). The radii of inside and outside turns are a = 50 mm and b = 100 mm respectively. The magnetic induction at the center of the spiral is
5 μT
7 μT
8 μT
10 μT
Three wires of equal lengths are bent in the form of loops. One of the loops is circle, another is a semi-circle and the third one is a square. They are placed in a uniform magnetic field and same electric current is passed through them. Which of the following loop configuration will experience greater torque?
Circle
Semi-circle
Square
All of them
Two identical coils, each with N turns and radius R are placed coaxially at a distance R as shown in the figure. If I is the current passing through the loops in the same direction, then the magnetic field at a point P which is at exactly at `"R"/2` distance between two coils is-

`(8"N"mu_circ"I")/(sqrt5"R")`
`(8"N"mu_circ"I")/(5^(3/2)"R")`
`(8"N"mu_circ"I")/(5"R")`
`(4"N"mu_circ"I")/(sqrt5"R")`
A wire of length l carrying a current I along the Y direction is kept in a magnetic field given by `vec"B" = beta/sqrt3 (hat"i" + hat"j" + hat"k")`T. The magnitude of Lorentz force acting on the wire is
`sqrt(2/3)beta"I"l`
`sqrt(1/3)beta"I"l`
`sqrt2 beta"I"l`
`sqrt(1/2)beta"I"l`
A bar magnet of length l and magnetic moment pm is bent in the form of an arc as shown in figure. The new magnetic dipole moment will be-
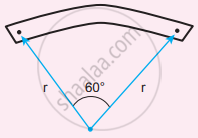
pm
\[\frac{3}{\pi}p_m\]
\[\frac{2}{\pi}p_m\]
\[\frac{1}{2}p_m\]
A non-conducting charged ring of charge q, mass m and radius r is rotated with constant angular speed ω. Find the ratio of its magnetic moment with angular momentum is
`"q"/"m"`
`"2q"/"m"`
`"q"/"2m"`
`"q"/"4m"`
The BH curve for a ferromagnetic material is shown in the figure. The material is placed inside a long solenoid which contains 1000 turns/cm. The current that should be passed in the solenonid to demagnetize the ferromagnet completely is
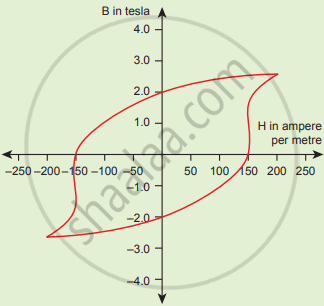
1.00 m A
1.25 mA
1.50 mA
1.75 mA
Two short bar magnets have magnetic moments 1.20 Am2 and 1.00 Am2respectively. They are kept on a horizontal table parallel to each other with their north poles pointing towards the south. They have a common magnetic equator and are separated by a distance of 20.0 cm. The value of the resultant horizontal magnetic induction at the mid-point O of the line joining their centers is (Horizontal components of Earth’s magnetic induction is 3.6 x 10-5 Wb m-2) (NSEP 2000-2001)
3.60 x 10-5 Wb m-1
3.5 x 10-5 Wb m-1
2.56 x 10-4 Wb m-1
2.2 x 10-4 Wb m-1
The vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field at a place is equal to the horizontal component. What is the value of angle of dip at this place?
30°
45°
60°
90°
A flat dielectric disc of radius R carries an excess charge on its surface. The surface charge density is σ. The disc rotates about an axis perpendicular to its plane passing through the centre with angular velocity ω. Find the magnitude of the torque on the disc if it is placed in a uniform magnetic field whose strength is B which is directed perpendicular to the axis of rotation
`1/4`σωπBR
`1/4`σωπBR2
`1/4`σωπBR3
`1/4`σωπBR4
The potential energy òf magnetic dipole whose dipole moment is `vec"p"_"m" = (- 0.5 hat"i" + 0.4 hat"j")"Am"^2` kept in uniform magnetic field `vec"B" = 0.2hat"i"`T
- 0.1 J
- 0.8 J
0.1 J
0.8 J
Short answer questions:
What is meant by magnetic induction?
Define magnetic flux.
Define magnetic dipole moment.
State Coulomb’s inverse law.
What is magnetic susceptibility?
State Biot-Savart’s law.
What is magnetic permeability?
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Compare dia, para and ferromagnetism.
What is meant by hysteresis?
Define magnetic declination.
Define magnetic inclination.
What is resonance condition in cyclotron?
Define ampere.
State Fleming’s left-Hand rule.
Is an ammeter connected in series or parallel in a circuit? Why?
Explain the concept of velocity selector.
Why is the path of a charged particle not a circle when its velocity is not perpendicular to the magnetic field?
Give the properties of dia/para/ferromagnetic materials.
What happens to the domains in a ferromagnetic material in the presence of external magnetic field?
How is a galvanometer converted into
- an ammeter and
- a voltmeter?
Long answer questions
Discuss Earth’s magnetic field in detail.
Deduce the relation for the magnetic induction at a point due to an infinitely long straight conductor carrying current.
Obtain a relation for the magnetic induction at a point along the axis of a circular coil carrying current.
Compute the torque experienced by a magnetic needle in a uniform magnetic field.
Calculate the magnetic field at a point on the axial line of a bar magnet.
Obtain the magnetic induction at a point on the equatorial line of a bar magnet. Magnetic field at a point along the equatorial line due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet).
Find the magnetic field due to a long straight conductor using Ampere’s circuital law.
Discuss the working of cyclotron in detail.
What is tangent law? Discuss in detail.
Derive the expression for the torque on a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field.
Discuss the conversion of galvanometer into an ammeter and also a voltmeter.
Calculate the magnetic field inside and outside of the long solenoid using Ampere’s circuital law
Derive the expression for the force between two parallel, current-carrying conductors.
Give an account of magnetic Lorentz force.
Compare the properties of soft and hard ferromagnetic materials.
Derive the expression for the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
Numerical problems
A bar magnet having a magnetic moment `vec"M"` is cut into four pieces i.e., first cut in two pieces along the axis of the magnet and each piece is further cut into two pieces. Compute the magnetic moment of each piece.
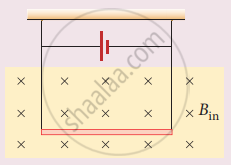
A conductor of linear mass density 0.2 g m1 suspended by two flexible wire as shown in figure. Suppose the tension in the supporting wires is zero when it is kept inside the magnetic field of I T whose direction is into the page. Compute the current inside the conductor and also the direction for the current. Assume g = 10 m s-2.
A circular coil with a cross-sectional area 0.1 cm2 is kept in a uniform magnetic field of strength 0.2 T. If the current passing in the coil is 3 A and the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the direction of a magnetic field. Calculate
- total torque on the coil
- total force on the coil
- average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field. (The free electron density for the material of the wire is 1028 m-3).
A bar magnet is placed in a uniform magnetic field whose strength is 0.8 T. If the bar magnet is oriented at an angle 30° with the external field experiences a torque of 0.2 Nm. Calculate
- the magnetic moment of the magnet
- the work is done by the magnetic field in moving it from the most stable configuration to the most its configuration and also compute the work done by the applied magnetic field in this case.
A non – conducting sphere has a mass of 100 g and radius 20 cm. A flat compact coil of wire with turns 5 is wrapped tightly around it with each turns concentric with the sphere. This sphere is placed on an inclined plane such that plane of coil is parallel to the inclined plane. A uniform magnetic field of 0.5 T exists in the region in a vertically upward direction. Compute the current 1 required to rest the sphere in equilibrium.
Calculate the magnetic field at the center of a square loop which carries a current of 1.5 A, length of each loop is 50 cm.
Solutions for 3: Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 3 - Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 3 - Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 3 - Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 3 (Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 3 Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current are Introduction to Magnetism, Coulomb’s Inverse Square Law of Magnetism, Torque Acting on a Bar Magnet in Uniform Magnetic Field, Magnetic Properties, Classification of Magnetic Materials, Hysteresis, Magnetic Effects of Current, Biot - Savart Law, Ampere’s Circuital Law, Lorentz Force, Torque on a Current Loop in Magnetic Field.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board solutions Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
