Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is magnetic permeability?
Solution
Magnetic permeability can be defined as the measure of the ability of the material to allow the passage of magnetic field lines through it or a measure of the capacity of the substance to take magnetisation or the degree of penetration of the magnetic field through the substance.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write Maxwell's generalization of Ampere's circuital law. Show that in the process of charging a capacitor, the current produced within the plates of the capacitor is `I=varepsilon_0 (dphi_E)/dt,`where ΦE is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates.
Electron drift speed is estimated to be of the order of mm s−1. Yet large current of the order of few amperes can be set up in the wire. Explain briefly.
A hollow tube is carrying an electric current along its length distributed uniformly over its surface. The magnetic field
(a) increases linearly from the axis to the surface
(b) is constant inside the tube
(c) is zero at the axis
(d) is zero just outside the tube.
Consider the situation described in the previous problem. Suppose the current i enters the loop at the points A and leaves it at the point B. Find the magnetic field at the centre of the loop.
The wires which connect the battery of an automobile to its starting motor carry a current of 300 A (for a short time). What is the force per unit length between the wires if they are 70 cm long and 1.5 cm apart? Is the force attractive or repulsive?
In a capillary tube, the water rises by 1.2 mm. The height of water that will rise in another capillary tube having half the radius of the first is:
A long solenoid having 200 turns per cm carries a current of 1.5 amp. At the centre of it is placed a coil of 100 turns of cross-sectional area 3.14 × 10−4 m2 having its axis parallel to the field produced by the solenoid. When the direction of current in the solenoid is reversed within 0.05 sec, the induced e.m.f. in the coil is:
Ampere's circuital law is used to find out ______
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
Consider the experimental set-up shown in the figure. This jumping ring experiment is an outstanding demonstration of some simple laws of Physics. A conducting non-magnetic ring is placed over the vertical core of a solenoid. When current is passed through the solenoid, the ring is thrown off. |
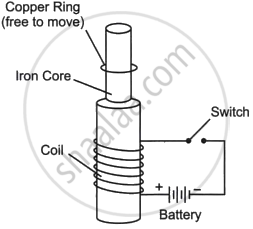
- Explain the reason for the jumping of the ring when the switch is closed in the circuit.
- What will happen if the terminals of the battery are reversed and the switch is closed? Explain.
- Explain the two laws that help us understand this phenomenon.
When current flowing through a solenoid decreases from 5A to 0 in 20 milliseconds, an emf of 500V is induced in it.
- What is this phenomenon called?
- Calculate coefficient of self-inductance of the solenoid.
