Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A hollow tube is carrying an electric current along its length distributed uniformly over its surface. The magnetic field
(a) increases linearly from the axis to the surface
(b) is constant inside the tube
(c) is zero at the axis
(d) is zero just outside the tube.
Solution
(b) is constant inside the tube
(c) is zero at the axis
A hollow tube is carrying uniform electric current along its length, so the current enclosed inside the tube is zero.
According to Ampere's law,
\[\oint \vec{B} . d \vec{l} = \mu_o i_{\text{inside}} \]
\[\text{ Inside the tube }, \]
\[\oint \vec{B} . d \vec{l} = 0, r < R\]
\[ \Rightarrow B_{\text{inside}} = \text{ Constant}\]
\[ \Rightarrow B_{\text{axis}} = 0 \]
The magnetic fields from points on the circular surface will point in opposite directions and cancel each other.
Outside the tube,
\[B \times 2\pi r = \mu_o i\]
\[ \Rightarrow B_{\text{outside}} = \frac{\mu_o i}{2\pi r}, r > R\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write Maxwell's generalization of Ampere's circuital law. Show that in the process of charging a capacitor, the current produced within the plates of the capacitor is `I=varepsilon_0 (dphi_E)/dt,`where ΦE is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates.
State Ampere’s circuital law.
State Ampere’s circuital law.
A 3.0 cm wire carrying a current of 10 A is placed inside a solenoid perpendicular to its axis. The magnetic field inside the solenoid is given to be 0.27 T. What is the magnetic force on the wire?
Explain Ampere’s circuital law.
A long straight wire of a circular cross-section of radius ‘a’ carries a steady current ‘I’. The current is uniformly distributed across the cross-section. Apply Ampere’s circuital law to calculate the magnetic field at a point ‘r’ in the region for (i) r < a and (ii) r > a.
A thin but long, hollow, cylindrical tube of radius r carries i along its length. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance r/2 from the surface (a) inside the tube (b) outside the tube.
A long, cylindrical wire of radius b carries a current i distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point inside the wire at a distance a from the axis.
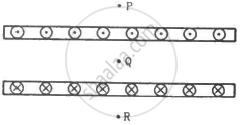
Two large metal sheets carry currents as shown in figure. The current through a strip of width dl is Kdl where K is a constant. Find the magnetic field at the points P, Q and R.
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Define ampere.
The wires which connect the battery of an automobile to its starting motor carry a current of 300 A (for a short time). What is the force per unit length between the wires if they are 70 cm long and 1.5 cm apart? Is the force attractive or repulsive?
A straight wire of diameter 0.5 mm carrying a current of 1 A is replaced by another wire of 1 mm diameter carrying the same current. The strength of the magnetic field far away is ______.
Ampere’s circuital law is given by _______.
In a capillary tube, the water rises by 1.2 mm. The height of water that will rise in another capillary tube having half the radius of the first is:
A long solenoid having 200 turns per cm carries a current of 1.5 amp. At the centre of it is placed a coil of 100 turns of cross-sectional area 3.14 × 10−4 m2 having its axis parallel to the field produced by the solenoid. When the direction of current in the solenoid is reversed within 0.05 sec, the induced e.m.f. in the coil is:
Two concentric and coplanar circular loops P and Q have their radii in the ratio 2:3. Loop Q carries a current 9 A in the anticlockwise direction. For the magnetic field to be zero at the common centre, loop P must carry ______.
Briefly explain various ways to increase the strength of the magnetic field produced by a given solenoid.
When current flowing through a solenoid decreases from 5A to 0 in 20 milliseconds, an emf of 500V is induced in it.
- What is this phenomenon called?
- Calculate coefficient of self-inductance of the solenoid.
