Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A 3.0 cm wire carrying a current of 10 A is placed inside a solenoid perpendicular to its axis. The magnetic field inside the solenoid is given to be 0.27 T. What is the magnetic force on the wire?
Solution
Length of the wire, l = 3 cm = 0.03 m
Current flowing in the wire, I = 10 A
Magnetic field, B = 0.27 T
Angle between the current and magnetic field, θ = 90°
Magnetic force exerted on the wire is given as:
F = Bl sin θ
= 0.27 × 10 × 0.03 sin 90°
= 8.1 × 10–2 N
Hence, the magnetic force on the wire is 8.1 × 10–2 N. The direction of the force can be obtained from Fleming’s left-hand rule.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Obtain an expression for magnetic induction along the axis of the toroid.
Explain Ampere’s circuital law.
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a long solenoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis ?
A long, straight wire carries a current. Is Ampere's law valid for a loop that does not enclose the wire, or that encloses the wire but is not circular?
A thin but long, hollow, cylindrical tube of radius r carries i along its length. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance r/2 from the surface (a) inside the tube (b) outside the tube.
A solid wire of radius 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnetic field B at a point at a distance (a) 2 cm (b) 10 cm and (c) 20 cm away from the axis. Sketch a graph B versus x for 0 < x < 20 cm.
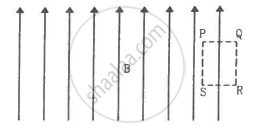
Sometimes we show an idealised magnetic field which is uniform in a given region and falls to zero abruptly. One such field is represented in figure. Using Ampere's law over the path PQRS, show that such a field is not possible.
What is magnetic permeability?
State Ampere’s circuital law.
In a capillary tube, the water rises by 1.2 mm. The height of water that will rise in another capillary tube having half the radius of the first is:
Ampere's circuital law is used to find out ______
Two concentric and coplanar circular loops P and Q have their radii in the ratio 2:3. Loop Q carries a current 9 A in the anticlockwise direction. For the magnetic field to be zero at the common centre, loop P must carry ______.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
Consider the experimental set-up shown in the figure. This jumping ring experiment is an outstanding demonstration of some simple laws of Physics. A conducting non-magnetic ring is placed over the vertical core of a solenoid. When current is passed through the solenoid, the ring is thrown off. |
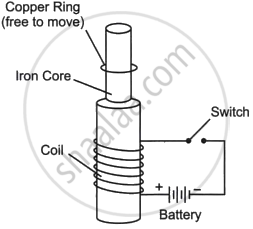
- Explain the reason for the jumping of the ring when the switch is closed in the circuit.
- What will happen if the terminals of the battery are reversed and the switch is closed? Explain.
- Explain the two laws that help us understand this phenomenon.
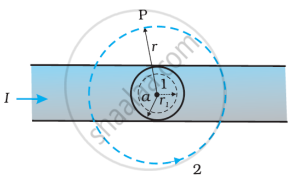
The given figure shows a long straight wire of a circular cross-section (radius a) carrying steady current I. The current I is uniformly distributed across this cross-section. Calculate the magnetic field in the region r < a and r > a.
When current flowing through a solenoid decreases from 5A to 0 in 20 milliseconds, an emf of 500V is induced in it.
- What is this phenomenon called?
- Calculate coefficient of self-inductance of the solenoid.
