Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 3.0 cm wire carrying a current of 10 A is placed inside a solenoid perpendicular to its axis. The magnetic field inside the solenoid is given to be 0.27 T. What is the magnetic force on the wire?
उत्तर
Length of the wire, l = 3 cm = 0.03 m
Current flowing in the wire, I = 10 A
Magnetic field, B = 0.27 T
Angle between the current and magnetic field, θ = 90°
Magnetic force exerted on the wire is given as:
F = Bl sin θ
= 0.27 × 10 × 0.03 sin 90°
= 8.1 × 10–2 N
Hence, the magnetic force on the wire is 8.1 × 10–2 N. The direction of the force can be obtained from Fleming’s left-hand rule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a long solenoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis ?
In Ampere's \[\oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{l} = \mu_0 i,\] the current outside the curve is not included on the right hand side. Does it mean that the magnetic field B calculated by using Ampere's law, gives the contribution of only the currents crossing the area bounded by the curve?
A hollow tube is carrying an electric current along its length distributed uniformly over its surface. The magnetic field
(a) increases linearly from the axis to the surface
(b) is constant inside the tube
(c) is zero at the axis
(d) is zero just outside the tube.
A thin but long, hollow, cylindrical tube of radius r carries i along its length. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance r/2 from the surface (a) inside the tube (b) outside the tube.
A long, cylindrical tube of inner and outer radii a and b carries a current i distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnitude of the magnitude filed at a point (a) just inside the tube (b) just outside the tube.
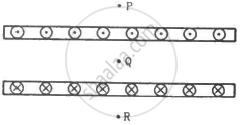
Two large metal sheets carry currents as shown in figure. The current through a strip of width dl is Kdl where K is a constant. Find the magnetic field at the points P, Q and R.
Define ampere.
Find the magnetic field due to a long straight conductor using Ampere’s circuital law.
The wires which connect the battery of an automobile to its starting motor carry a current of 300 A (for a short time). What is the force per unit length between the wires if they are 70 cm long and 1.5 cm apart? Is the force attractive or repulsive?
A straight wire of diameter 0.5 mm carrying a current of 1 A is replaced by another wire of 1 mm diameter carrying the same current. The strength of the magnetic field far away is ______.
Ampere’s circuital law is given by _______.
Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C, then which statement is correct?
In a capillary tube, the water rises by 1.2 mm. The height of water that will rise in another capillary tube having half the radius of the first is:
A long solenoid having 200 turns per cm carries a current of 1.5 amp. At the centre of it is placed a coil of 100 turns of cross-sectional area 3.14 × 10−4 m2 having its axis parallel to the field produced by the solenoid. When the direction of current in the solenoid is reversed within 0.05 sec, the induced e.m.f. in the coil is:
A thick current carrying cable of radius ‘R’ carries current ‘I’ uniformly distributed across its cross-section. The variation of magnetic field B(r) due to the cable with the distance ‘r’ from the axis of the cable is represented by ______
Two concentric and coplanar circular loops P and Q have their radii in the ratio 2:3. Loop Q carries a current 9 A in the anticlockwise direction. For the magnetic field to be zero at the common centre, loop P must carry ______.
Briefly explain various ways to increase the strength of the magnetic field produced by a given solenoid.
