Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two long and parallel straight wires A and B carrying currents of 8.0 A and 5.0 A in the same direction are separated by a distance of 4.0 cm. Estimate the force on a 10 cm section of wire A.
उत्तर
Current flowing in wire A, IA = 8.0 A
Current flowing in wire B, IB = 5.0 A
Distance between the two wires, r = 4.0 cm = 0.04 m
Length of a section of wire A, l = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Force exerted on length l due to the magnetic field is given as:
B = `(mu_0 2"I"_"A""I"_"B""I")/(4pi"r")`
Where,
`mu_0` = Permeability of free space = 4π × 10–7 T m A–1
B = `(4pi xx 10^-7 xx 2 xx 8 xx 5 xx 0.1)/(4pi xx 0.04)`
= 2 × 10–5 N
The magnitude of the force is 2 × 10–5 N. This is an attractive force normal to A towards B because the direction of the currents in the wires is the same.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two infinitely long straight parallel wires, '1' and '2', carrying steady currents I1 and I2 in the same direction are separated by a distance d. Obtain the expression for the magnetic field `vecB`due to the wire '1' acting on wire '2'. Hence find out, with the help of a suitable diagram, the magnitude and direction of this force per unit length on wire '2' due to wire '1'. How does the nature of this force changes if the currents are in opposite direction? Use this expression to define the S.I. unit of current.
Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying conductors, define one ampere of current.
The figure shows three infinitely long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Find the
(i) magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point A lying on conductor 1,
(ii) magnetic force on conductor 2.

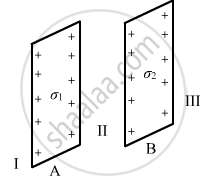
Two infinitely large plane thin parallel sheets having surface charge densities σ1 and σ2 (σ1 > σ2) are shown in the figure. Write the magnitudes and directions of the net fields in the regions marked II and III.
A long, straight wire carries a current along the z-axis, One can find two points in the x−y plane such that
(a) the magnetic fields are equal
(b) the directions of the magnetic fields are the same
(c) the magnitudes of the magnetic fields are equal
(d) the field at one point is opposite to that at the other point.
A current of 10 A is established in a long wire along the positive z-axis. Find the magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] at the point (1 m, 0, 0).
A hypothetical magnetic field existing in a region is given by `vecB = B_0 vece` where `vece`_r denotes the unit vector along the radial direction. A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed with its plane parallel to the x−y plane and the centre at (0, 0, d). Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the loop.
A straight wire of length l can slide on two parallel plastic rails kept in a horizontal plane with a separation d. The coefficient of friction between the wire and the rails is µ. If the wire carries a current i, what minimum magnetic field should exist in the space in order to slide the wire on the rails?
Figure shows a metallic wire of resistance 0.20 Ω sliding on a horizontal, U-shaped metallic rail. The separation between the parallel arms is 20 cm. An electric current of 2.0 µA passes through the wire when it is slid at a rate of 20 cm s−1. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 3.0 × 10−5 T, calculate the dip at the place.
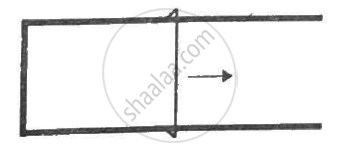
Figure shows two parallel wires separated by a distance of 4.0 cm and carrying equal currents of 10 A along opposite directions. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the points A1, A2, A3.

If a current I is flowing in a straight wire parallel to x-axis and magnetic field is there in the y-axis then, ______.
According to Ampere's circuital law, ______.
A milli voltmeter of 25 milli volt range is to be converted into an ammeter of 25 ampere range. The value (in ohm) of necessary shunt will be ______.
The nature of parallel and anti-parallel currents are ______.
Two long straight parallel conductors carrying currents I1 and I2 are separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field produced by one exerts an attractive force on the other. Obtain the expression for this force and hence define 1 ampere.
Two long parallel wires kept 2 m apart carry 3A current each, in the same direction. The force per unit length on one wire due to the other is ______.
The figure below are two long, parallel wires carrying current in the same direction such that I1 < I2.
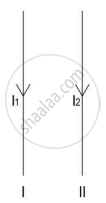
- In which direction will wire I1 move?
- If the direction of the current I2 is reversed, in which direction will the wire I1 move now?
