Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A straight wire of length l can slide on two parallel plastic rails kept in a horizontal plane with a separation d. The coefficient of friction between the wire and the rails is µ. If the wire carries a current i, what minimum magnetic field should exist in the space in order to slide the wire on the rails?
उत्तर
Given:
Length of the wire = l
Distance between the plastic rails = d
The coefficient of friction between the wire and the rails = µ
Electric current flowing through the wire = i
The minimum magnetic field that should exist in the space in order to slide the wire on the rails should be such that the net magnetic force acting on the wire is equal to the frictional force on the wire.
F = µmg
F = µR
where
µ is the coefficient of friction between the wire and the rail
R is the normal reaction force
F is the magnetic force
µMg = iBl
`B = (muMg)/(il)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying conductors, define one ampere of current.
What is the magnitude of magnetic force per unit length on a wire carrying a current of 8 A and making an angle of 30° with the direction of a uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T?
Two long and parallel straight wires A and B carrying currents of 8.0 A and 5.0 A in the same direction are separated by a distance of 4.0 cm. Estimate the force on a 10 cm section of wire A.
The figure shows three infinitely long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Find the
(i) magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point A lying on conductor 1,
(ii) magnetic force on conductor 2.

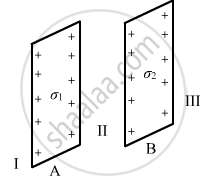
Two infinitely large plane thin parallel sheets having surface charge densities σ1 and σ2 (σ1 > σ2) are shown in the figure. Write the magnitudes and directions of the net fields in the regions marked II and III.
and ```vecE` and `vecB`denote electric and magnetic fields in a frame S and `vecE`→ and `vecB` in another frame S' moving with respect to S at a velocity `vecV` Two of the following equations are wrong. Identify them.
(a) `B_y^, = B_y + (vE_z)/c^2`
(b) `E_y^' = E_y - (vB_z)/(c^2)`
`(c) Ey = By + vE_z`
`(d) E_y = E_y + vB_z`
Two parallel, long wires carry currents i1 and i2 with i1 > i2. When the currents are in the same direction, the magnetic field at a point midway between the wires is 10 µT. If the direction of i2 is reversed, the field becomes 30 µT. The ratio i1/i2 is
A long, straight wire carries a current along the z-axis, One can find two points in the x−y plane such that
(a) the magnetic fields are equal
(b) the directions of the magnetic fields are the same
(c) the magnitudes of the magnetic fields are equal
(d) the field at one point is opposite to that at the other point.
A long, straight wire of radius R carries a current distributed uniformly over its cross section. T he magnitude of the magnetic field is
(a) maximum at the axis of the wire
(b) minimum at the axis of the wire
(c) maximum at the surface of the wire
(d) minimum at the surface of the wire.
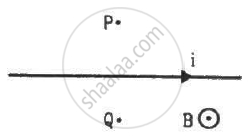
A long, straight wire carrying a current of 1.0 A is placed horizontally in a uniform magnetic field B = 1.0 × 10−5 T pointing vertically upward figure. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at the points P and Q, both situated at a distance of 2.0 cm from the wire in the same horizontal plane.
The magnetic field existing in a region is given by `vecB = B_0(1 + x/1)veck` . A square loop of edge l and carrying a current i, is placed with its edges parallel to the x−y axes. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic force experienced by the loop.
A rectangular coil of 100 turns has length 5 cm and width 4 cm. It is placed with its plane parallel to a uniform magnetic field and a current of 2 A is sent through the coil. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B if the torque acting on the coil is 0.2 N m−1
Figure shows a metallic wire of resistance 0.20 Ω sliding on a horizontal, U-shaped metallic rail. The separation between the parallel arms is 20 cm. An electric current of 2.0 µA passes through the wire when it is slid at a rate of 20 cm s−1. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 3.0 × 10−5 T, calculate the dip at the place.
According to Ampere's circuital law, ______.
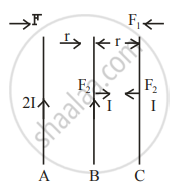
Three infinitely long parallel straight current-carrying wires A, B and C are kept at equal distance from each other as shown in the figure. The wire C experiences net force F. The net force on wire C, when the current in wire A is reversed will be ______.
Do magnetic forces obey Newton’s third law. Verify for two current elements dl1 = dlî located at the origin and dl2 = dlĵ located at (0, R, 0). Both carry current I.
Five long wires A, B, C, D and E, each carrying current I are arranged to form edges of a pentagonal prism as shown in figure. Each carries current out of the plane of paper.
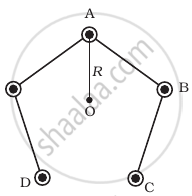
- What will be magnetic induction at a point on the axis O? AxisE is at a distance R from each wire.
- What will be the field if current in one of the wires (say A) is switched off?
- What if current in one of the wire (say) A is reversed?
