Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Five long wires A, B, C, D and E, each carrying current I are arranged to form edges of a pentagonal prism as shown in figure. Each carries current out of the plane of paper.
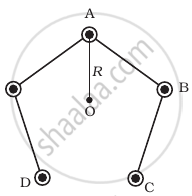
- What will be magnetic induction at a point on the axis O? AxisE is at a distance R from each wire.
- What will be the field if current in one of the wires (say A) is switched off?
- What if current in one of the wire (say) A is reversed?
उत्तर
a. The wires shown in this problem carrying current outwards to the plane. And we know that direction of magnetic field is perpendicular to both current and position vector r. So, the vector sum of magnetic field produced by each wire at O is equal to 0.
Suppose the five wires A, B, C, D and E be perpendicular to the plane of paper at locations as shown in figure.
Thus, magnetic field induction due to five wires will be represented by various sides of closed pentagon in one order, lying in the plane of paper. So, its value is zero.
b. When current in AA' is switched off, then B1 = 0 and resultant becomes
R = B2 + B3 + B4 + B5
But form (a) part B1 + B2 + B3 + B4 + B5 = 0
Or `vecB_2 + vecB_3 + vecB_4 + vecB_5 = - vecB_1`
R = – B1
R = `(mu_0I)/(2pir)`
i.e. Direction of resultant is opposite to `vecB_1`.
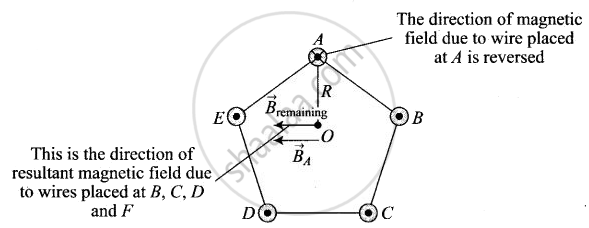
c. If current in wire A is reversed, then
Total magnetic field induction at O = Magnetic field induction due to A + Magnetic field induction due to wires B, C, D and E
= `(mu_0)/(4piR) (2I)/R` (acting perpendicular to AO towards left) + `(mu_0)/pi (2I)/R` (acting perpendicular AO towards left)
= `(mu_0I)/(piR)` acting perpendicular AO towards left.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two long and parallel straight wires A and B carrying currents of 8.0 A and 5.0 A in the same direction are separated by a distance of 4.0 cm. Estimate the force on a 10 cm section of wire A.
A charged particle goes undeflected in a region containing an electric and a magnetic field. It is possible that
(a) `vecE" || "vecB , vecv" || " vec E `
(b) `vecE "is not parallel" vecB`
(c) `vecv " || " vecB but vecv "is not parallel"`
(d) `vecE" || " vecB but vecv "is not parallel"`
A hypothetical magnetic field existing in a region is given by `vecB = B_0 vece` where `vece`_r denotes the unit vector along the radial direction. A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed with its plane parallel to the x−y plane and the centre at (0, 0, d). Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the loop.
Figure shows a metallic wire of resistance 0.20 Ω sliding on a horizontal, U-shaped metallic rail. The separation between the parallel arms is 20 cm. An electric current of 2.0 µA passes through the wire when it is slid at a rate of 20 cm s−1. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 3.0 × 10−5 T, calculate the dip at the place.
Two parallel wires carry equal currents of 10 A along the same direction and are separated by a distance of 2.0 cm. Find the magnetic field at a point which is 2.0 cm away from each of these wires.
Consider a 10-cm long piece of a wire which carries a current of 10 A. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field due to the piece at a point which makes an equilateral triangle with the ends of the piece.
Three coplanar parallel wires, each carrying a current of 10 A along the same direction, are placed with a separation 5.0 cm between the consecutive ones. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force per unit length acting on the wires.
A milli voltmeter of 25 milli volt range is to be converted into an ammeter of 25 ampere range. The value (in ohm) of necessary shunt will be ______.
Equal currents are passing through two very long and straight parallel wires in the same direction. They will ______
Two long parallel wires kept 2 m apart carry 3A current each, in the same direction. The force per unit length on one wire due to the other is ______.
