Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the magnitude of magnetic force per unit length on a wire carrying a current of 8 A and making an angle of 30° with the direction of a uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T?
उत्तर

Current in the wire, I = 8 A
Magnitude of the uniform magnetic field, B = 0.15 T
Angle between the wire and magnetic field, θ = 30°
Magnetic force per unit length on the wire is given as:
f = BI sinθ
= 0.15 × 8 × 1 × sin 30°
= 0.6 N m–1
Hence, the magnetic force per unit length on the wire is 0.6 N m–1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying conductors, define one ampere of current.
Two long and parallel straight wires A and B carrying currents of 8.0 A and 5.0 A in the same direction are separated by a distance of 4.0 cm. Estimate the force on a 10 cm section of wire A.
The figure shows three infinitely long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Find the
(i) magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point A lying on conductor 1,
(ii) magnetic force on conductor 2.

Two long straight parallel conductors 'a' and 'b', carrying steady currents Ia and Ib are separated by a distance d. Write the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field produced by the conductor 'a' at the points along the conductor 'b'. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, what is the nature and magnitude of the force between the two conductors?
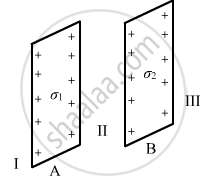
Two infinitely large plane thin parallel sheets having surface charge densities σ1 and σ2 (σ1 > σ2) are shown in the figure. Write the magnitudes and directions of the net fields in the regions marked II and III.
A charged particle goes undeflected in a region containing an electric and a magnetic field. It is possible that
(a) `vecE" || "vecB , vecv" || " vec E `
(b) `vecE "is not parallel" vecB`
(c) `vecv " || " vecB but vecv "is not parallel"`
(d) `vecE" || " vecB but vecv "is not parallel"`
Two parallel, long wires carry currents i1 and i2 with i1 > i2. When the currents are in the same direction, the magnetic field at a point midway between the wires is 10 µT. If the direction of i2 is reversed, the field becomes 30 µT. The ratio i1/i2 is
A long, straight wire carries a current along the z-axis, One can find two points in the x−y plane such that
(a) the magnetic fields are equal
(b) the directions of the magnetic fields are the same
(c) the magnitudes of the magnetic fields are equal
(d) the field at one point is opposite to that at the other point.
The magnetic field existing in a region is given by `vecB = B_0(1 + x/1)veck` . A square loop of edge l and carrying a current i, is placed with its edges parallel to the x−y axes. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic force experienced by the loop.
A long, straight wire carries a current i. Let B1 be the magnetic field at a point P at a distance d from the wire. Consider a section of length l of this wire such that the point P lies on a perpendicular bisector of the section B2 be the magnetic field at this point due to this second only. Find the value of d/l so that B2 differs from B1 by 1%.
Three coplanar parallel wires, each carrying a current of 10 A along the same direction, are placed with a separation 5.0 cm between the consecutive ones. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force per unit length acting on the wires.
Define Ampere in terms of force between two current carrying conductors.
A milli voltmeter of 25 milli volt range is to be converted into an ammeter of 25 ampere range. The value (in ohm) of necessary shunt will be ______.
Equal currents are passing through two very long and straight parallel wires in the same direction. They will ______
Beams of electrons and protons move parallel to each other in the same direction. They ______.
The figure below are two long, parallel wires carrying current in the same direction such that I1 < I2.
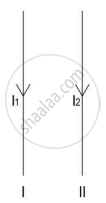
- In which direction will wire I1 move?
- If the direction of the current I2 is reversed, in which direction will the wire I1 move now?
