Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In Ampere's \[\oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{l} = \mu_0 i,\] the current outside the curve is not included on the right hand side. Does it mean that the magnetic field B calculated by using Ampere's law, gives the contribution of only the currents crossing the area bounded by the curve?
उत्तर
In Ampere's law \[\oint \vec{B} . \vec{dl} = \mu_o i\] , i is the total current crossing the area bounded by the closed curve. The magnetic field B on the left-hand side is the resultant field due to all existing currents.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Explain Ampere’s circuital law.
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a long solenoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis ?
In order to have a current in a long wire, it should be connected to a battery or some such device. Can we obtain the magnetic due to a straight, long wire by using Ampere's law without mentioning this other part of the circuit?
A hollow tube is carrying an electric current along its length distributed uniformly over its surface. The magnetic field
(a) increases linearly from the axis to the surface
(b) is constant inside the tube
(c) is zero at the axis
(d) is zero just outside the tube.
A long, cylindrical wire of radius b carries a current i distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point inside the wire at a distance a from the axis.
What is magnetic permeability?
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Define ampere.
Find the magnetic field due to a long straight conductor using Ampere’s circuital law.
Calculate the magnetic field inside and outside of the long solenoid using Ampere’s circuital law
A straight wire of diameter 0.5 mm carrying a current of 1 A is replaced by another wire of 1 mm diameter carrying the same current. The strength of the magnetic field far away is ______.
Ampere’s circuital law is given by _______.
In a capillary tube, the water rises by 1.2 mm. The height of water that will rise in another capillary tube having half the radius of the first is:
The force required to double the length of a steel wire of area 1 cm2, if it's Young's modulus Y = `2 xx 10^11/m^2` is:
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
Consider the experimental set-up shown in the figure. This jumping ring experiment is an outstanding demonstration of some simple laws of Physics. A conducting non-magnetic ring is placed over the vertical core of a solenoid. When current is passed through the solenoid, the ring is thrown off. |
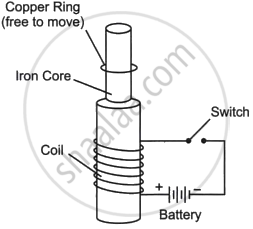
- Explain the reason for the jumping of the ring when the switch is closed in the circuit.
- What will happen if the terminals of the battery are reversed and the switch is closed? Explain.
- Explain the two laws that help us understand this phenomenon.
Briefly explain various ways to increase the strength of the magnetic field produced by a given solenoid.
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain an expression for magnetic flux density ‘B’ at a point near an infinitely long and straight conductor, carrying a current I.
