Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is magnetic permeability?
उत्तर
Magnetic permeability can be defined as the measure of the ability of the material to allow the passage of magnetic field lines through it or a measure of the capacity of the substance to take magnetisation or the degree of penetration of the magnetic field through the substance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A long, straight wire carries a current. Is Ampere's law valid for a loop that does not enclose the wire, or that encloses the wire but is not circular?
In order to have a current in a long wire, it should be connected to a battery or some such device. Can we obtain the magnetic due to a straight, long wire by using Ampere's law without mentioning this other part of the circuit?
A solid wire of radius 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnetic field B at a point at a distance (a) 2 cm (b) 10 cm and (c) 20 cm away from the axis. Sketch a graph B versus x for 0 < x < 20 cm.
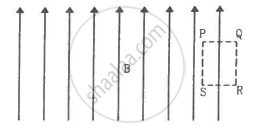
Sometimes we show an idealised magnetic field which is uniform in a given region and falls to zero abruptly. One such field is represented in figure. Using Ampere's law over the path PQRS, show that such a field is not possible.
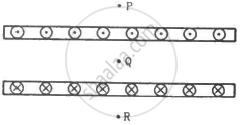
Two large metal sheets carry currents as shown in figure. The current through a strip of width dl is Kdl where K is a constant. Find the magnetic field at the points P, Q and R.
A solenoid of length 0.6 m has a radius of 2 cm and is made up of 600 turns If it carries a current of 4 A, then the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid is:
A long solenoid having 200 turns per cm carries a current of 1.5 amp. At the centre of it is placed a coil of 100 turns of cross-sectional area 3.14 × 10−4 m2 having its axis parallel to the field produced by the solenoid. When the direction of current in the solenoid is reversed within 0.05 sec, the induced e.m.f. in the coil is:
Ampere's circuital law is used to find out ______
Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C ______.
- `oint B.dl = +- 2μ_0I`
- the value of `oint B.dl` is independent of sense of C.
- there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular.
- B vanishes everywhere on C.
Two concentric and coplanar circular loops P and Q have their radii in the ratio 2:3. Loop Q carries a current 9 A in the anticlockwise direction. For the magnetic field to be zero at the common centre, loop P must carry ______.
